CHM1 16 Gibbs Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant Collectio
Tags | |
UUID | 19e48d21-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Gibbs Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant
From UCDavis Chemwiki
ΔG: Gibbs Free Energy
ΔG is the change of Gibbs (free) energy for a system and ΔG° is the Gibbs energy change for a system under standard conditions (1 atm, 298K). On an energy diagram, DeltaG can be represented as:
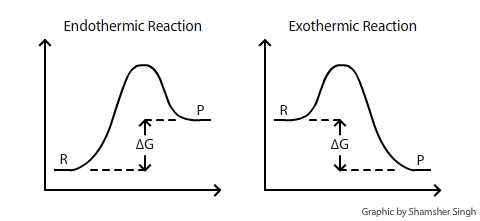
Where DeltaG is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. In addition DeltaG is unaffected by external factors that change the kinetics of the reaction. For example if Ea(activation energy) were to decrease in the presence of a catalyst or the kinetic energy of molecules increases due to a rise in temperature, the DeltaG value would remain the same.
K: The Equilibrium Constant
K is the equilibrium constant of a reaction and is given by the reaction quotient:
`aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD`
K = ([A]^a [B]^b)/([C]^c [D]^d)
The connection between Gibbs free energy and constant equilibrium are directly related in the following equation:
- R = 8.314 J mol C^(-1)
- `T = Temperature in K`
- n = "moles of "e^(-)" in a balanced redox reaction."
- `F = "Faraday's Constant" = 96,485 C"/mol"`
These relationships are summarized as follows:
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0 | K | Product Formation |
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0 < 0` | K > 1 | Products favored over reactants at equilibrium. |
| DeltaG_"rxn"^0= 0 | K = 1 | At equilibrium when [C]c[D]d…= [A]a[B]b…(very rare) |
| DeltaG_"rxn"^0 > 0 | K < 1 | Reactants favored over products at equilibrium |
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
