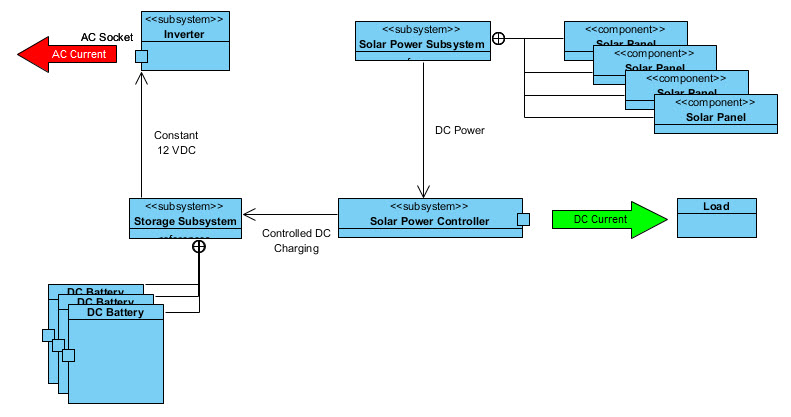
Components of a Solar Solution
Tags | |
UUID | 1cca6bb5-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Introduction to the Parts of a Solar Power System
In a system designed to capture electrical energy generated by solar panels we pay close attention to compatibility of subsystem attributes. Key subsystems we will discuss are:
- storage (batteries)
- solar power (solar panels)
- solar power controller (power manager)
- inverters (DC to AC converter)
These subsystems combine to make the electricity produced by our solar-powered system compatible with contemporary household devices. In Figure 1 the AC current produced on the left from the Inverter is the current one would plug common household devices into.
|
|
Figure 1: Subsystem Components of a Solar-powered System |
Basic Subsystem Functions
Energy is created in our local system by the Solar Power Subsystem shown in Figure 1 above.
Of course, the energy is really created within the massive fusion reactor we call the Sun and is transmitted to the solar panel through space as the energy of electromagnetic waves. And the Sun's fusion energy is, in turn, the result of the Big Bang dispersing cosmic debris throughout our galaxy, which a little later coalesced into that big glowing ball, again the one we call the Sun.
The Sun's radiant electromagnetic energy incident on our fly-speck of a solar panel is converted to electrical energy inside a solar panel, a component of the Solar Power Subsystem. The Solar Power Subsystem is comprised of one or more Solar Panel components We will discuss the various ways we might connect the Solar Panels together (in series and in parallel circuits) in the vCalc Collection on "Solar Panel Configurations".
The Solar Power Controller subsystem is a complex device that optimizes how electricity is used to charge the batteries. The Solar Power Controller also optimizes the availability of energy to support any demands for electricity by devices we plug into the Inverter or connect as loads to the Solar Power Controller directly.
The use of batteries should be common knowledge in today's world but the types of batteries we use in our solar-powered system are much more sophisticated than the battery we typically use to start our car or the battery we insert into our flashlight. Regardless, the Storage Subsystem is comprised of one or more "deep-cycle" batteries, and we will discuss batteries further in the Collection titled "Battery Technology".
If we look at our Solar Powered System as a whole, the system functionally provides a Direct Current (DC) solar-power source. We connect our power source to an Inverter to transform the DC energy into Alternating Current (AC) energy for numerous practical applications, like:
- powering the computer I am using to create this vCalc Collection
- running a common household fan to cool me
- powering a refrigerator to keep my refreshments cold
- powering a ceiling light
- and many others
The electrical power generated by solar panels is produced as direct current (DC). DC electrical power is typically stored in batteries and can be used to power devices designed to run on DC current. A flashlight, for instance, runs on a household battery commonly of a standard type designated AA batteries, AAA batteries, C batteries, etc. There are small solar panels that can be purchased to charge these small batteries
In use of solar systems, which generate significantly more power than small household batteries you can hold in your palm, DC current is converted to AC current. AC is the common power source in most homes today and was invented by Nikola Tesla in the late 1880s. See vCalc's Tesla Collection for more on the genius of Nikola Tesla.
In subsequent discussions of the subsystems of the Solar Power System, we will refer back to the basic relationships between power, voltage and current discussed in earlier Collections in this series. This basic electrical principles will help us understand the physical architecture of the Solar Power System. To design a system or be able to specify the requirements for a contractor to install a system, you will want to understand the basic power needs and component design trades and all of these trades depend on these fundamental principles of electricity.
Solar energy system have several key components, but the most important component is, of course, the Sun (See Where is the Sun in All of This?). The sun emits a tremendous amount of radiation that traverses the 93 million miles (see Earth - mean distance from Sun) to reach the Earth. The radiation intensity falls off as the inverse square of the distance from the radiation source, the Sun, but the irradiance from the Sun is still measured at the outer boundary of the Earth's upper atmosphere to be something near .
Solar energy varies by season and by weather conditions but even on a cloudy day in the Winter there is a significant amount of energy being transmitted to the surface of the Earth.
Note, retail and commercial providers of solar panel technology often provide guidance on the selection and use of subsystem components, like this hyperlinked page.
Calculators and Collections
Equations
- Calculate Electric Potential (Volts) Carol Use Equation
- Electricity Consumption KurtHeckman Use Equation
- AWG Lookup MichaelBartmess Use Equation
- Voltage Drop KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Wire Gauge for Safe Voltage Drop KurtHeckman Use Equation
- Calculate Electric Current (Amperes) Carol Use Equation
Datasets
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |