What is a Solar Power System
Tags | |
UUID | 2b34af4e-e071-11eb-8eb2-bc764e203090 |
From the viewpoint of the retail consumer of the commercial components of a Solar Power System, the capabilities of the Solar Power System are fundamentally easy to understand. The Solar Power System receives sunlight from the Sun at the Solar Panels and converts the incident radiation to direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is delivered to a user to perform all kinds of work and simultaneously, in most solar power systems, this DC electricity is converted to alternating current (AC) electricity and made available for all kinds of common technology uses, from charging a cell phone to running a water pump.
DC is generally converted to AC, as DC suffers power losses over distance.
The Solar Power System typically also stores the energy in batteries to enable a continuous use of electricity, even when the Sun does not shine.
These simple use cases shown in Figure 1 comprise all that the system has to accomplish to satisfy the average electricity user's needs.
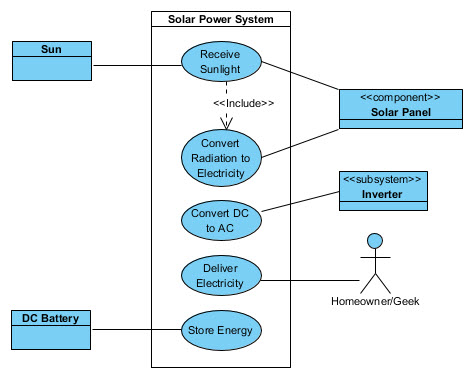
Figure 1: Use Cases for a Solar Power System
Continue on to get a look at the basic electrical equations that define how the Solar Power System achieves the proper current to provide commercial-grade electricity.
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
