Vector Sum of Forces (2D)
Tags | |
UUID | 0bf3c046-cde4-11e4-a3bb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Vector Sum of Forces (2D) calculator computes the sum of two vectors by summing the x and y components of the two vectors.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (→Fax) x component of vector A
- (→Fay) y component of vector A
- (→Fbx) x component of vector B
- (→Fby) y component of vector B
Vector Sum of Forces (2D) (→Fnet): The resulting vector is returned in Newtons.
The Math / Science
The Vector Sum of Forces (2D) equation computes the sum of two vectors by summing the x and y components of the two vectors.
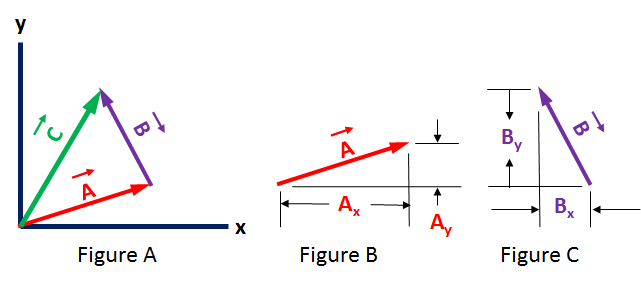
To simplify the graphical example we show vector →A begins at the origin of the Cartesian axes and so that vector →A points to the point [→Ax, →Ay]. Nevertheless, we know that these vectors and this vector addition can occur anywhere on the X/Y plane.
Notes
A vector is a mathematical concept of an object that has direction and length. A line alone is not a vector but a line with orientation spanning the distance between two points in space is a vector.
Figure A shows the vector summation: →C = →A + →B with →A having it's start at the origin for simplification.
Figure B shows the x and y components of vector →A (in red).
Figure C shows the x and y components of vector →B (in purple).
Vector →C's coordinates = [→Cx , →Cy] = [→Ax + →Bx, →Ay + →By]
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
