Tags | |
UUID | 29fa42ae-1de8-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
Bayes' Theorem, , computes the probability of event A occurring if event B is true. It is based in part on the idea that someone's personal experiences may affect their perception at the time they see the event. The event can be
Inputs
- P(A) is the probability of A being true independent of B
- P(B) is the probability of B being true independent of A
- P(B|A) is the probability of B being true if A has been observed (is true)
Probabilities
Probabilities are expressed here as decimals between 0 and 1, where 0 means there is no chance of an occurrence and 1 implies a certainty of occurrence. For example, an event with a 20% chance of occurrence has a probability of 0.2.
Ambiguous Images
Bayes' Theorem is particularly useful in the psychology field of perception.
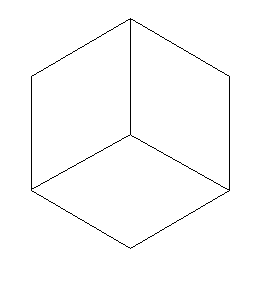 Ambiguous Cube/Room Figure
Ambiguous Cube/Room Figure
In this common optical illusion, the figure can be perceived as a cube or a room. Bayes' theorem can provide some insight as to what an individual is most likely to perceive, based on their prior experiences and current perspective. For example, a person who is, hypothetically, locked inside an empty room for an extended period of time is much more likely to perceive this figure as a room than someone who constantly perceives boxes and 3D corners.
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
