Tags | |
UUID | 4eb8e95d-3992-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The region III titration equation calculates the pH of the solution at the equivalence point, where a weak acid is titrated with a strong base.
Solving a titration problem, Region III: At the equivalence point.
Given: Formal concentration of weak acid and strong base, initial volume of weak acid, amount of strong base added Kw , Ka or pKa.
Equivalence point is where the weak acid and strong base are in equilibrium with each other. This can be illustrated by an ice table
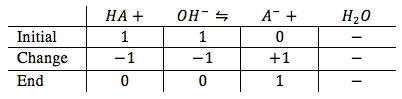
Since the weak acid and the strong base are in equilibrium, producing strong acid. We can flip the reaction and solve for hydroxide ion concentration to find the pH.
First we must find the diluted formal concentration of the weak acid, since strong base has been added and has reacted with the acid.
The diluted concentration can be calculated using the following equation
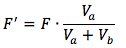
*Note: for the description of variables scroll down.
We can now use this new formal concentration to solve for the hydroxide ion concentration as we did before for region I of the titration
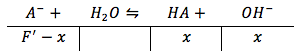
However, here we are solving for the hydroxide ion concentration oppose to the hydronium ion concentration, thus the equilibrium equation will be solved for base, thus Ka must be converted to Kb. This can be easily done by using the known fact that
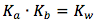
By rearranging the variables we can solve for Kb, the equilibrium equation then becomes
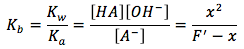
We can now solve for x, which is the same as the hydroxide ion concentration, by multiplying Kb by F' and taking the square root, the equation becomes as follows
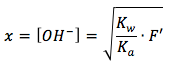
Notice that this is solved for the hydroxide ion and not hydronium ion, thus we can't plug this straight in to the pH equation just yet. We must convert it to the hydronium ion using this equation and plug it in to the pH equation. The final equation is
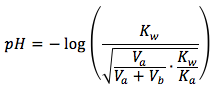
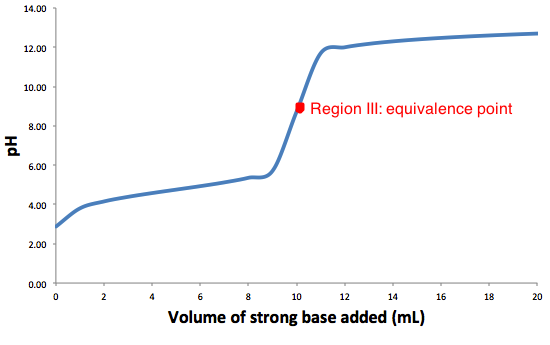
The graph above is the a typical weak acid-strong base titration, with the equivalence point represented.
Description
The equation is
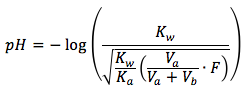
where
- Kw is the dissociation constant of water, which equals to 1.0x10-14
- Ka is the acid equilibrium constant, can be found here.
- Va is the initial volume of weak acid in the solution in units of (mL)
- Vb is the volume of strong base added in the solution in units of (mL)
- F is the formal concentration of weak acid in units of (mol/L)
References
Harris, 9th Edition. Pp.236-238
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
