Adjacent Side - Pythagorean Theorem
b2=√c2-a2
Tags | |
UUID | 52b26da4-0646-11e4-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
Adjacent Side - Pythagorean Theorem
This equation uses the Pythagorean Theorem to compute the length of one side of a right triangle adjacent to the right angle given inputs of the length of the other side and the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Notes
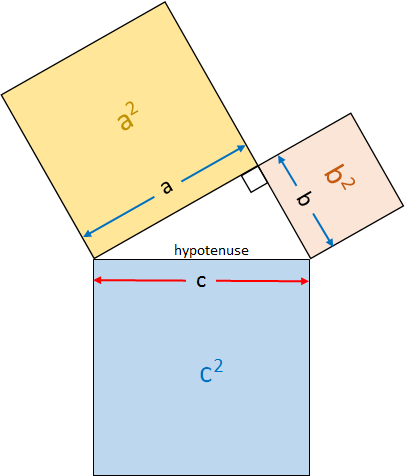
The Pythagorean Theorem is shown graphically in the picture. The sum of the area of the two squares whose sides are a and b (as shown in the picture) is equal to the area of the square whose side is equal to c. In this picture a right triangle is formed by one edges of each of the three squares. The hypotenuse of this right triangle has the length c.
In other words, this picture graphically portrays the Pythagorean Theorem: a2+b2=c2
This equation, Adjacent Side - Pythagorean Theorem, is used in 1 page
Calculators
•
KanisshhAreaa
by
Kanish254
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
