Processing...
`A = epsilonbc`
Enter a value for all fields
The Beer-Lambert's law or simply Beer's law calculates the absorptivity of a sample based on the analyte concentration, path length and the molar absorptivity of the analyte. Beer's law is highly useful in spectrophotometry. There are several conditions for when the law is applicable, 1) monochromatic radiation is used, 2) when the chromophore concentrations is less than ~0.01M, 3) when the absorbing species is not participating in a concentration dependent equilibrium.
Description
The equation is
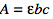
where
- ε is molar absorptivity in units of (L/mol cm)
- b is the path length in units of (cm)
- c is the concentration in units (mol/L)
Related Topics
- Absorbance (for the Spanish site click here)
- Transmittance (for the Spanish site click here)
References
Harris, 9th Edition. Pp.436
SaveSaveSaveSaveSaveSave