Tags | |
UUID | 632ac292-38b7-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The region II titration equation calculates the pH of the solution before the equivalence point is reached.
Solving a titration problem, Region II: Before the equivalence point.
Given: Formal concentration of the weak acid and strong base, the amount of strong base is added to the acid, pKa and or Ka.
Frist solve for equivalence volume.
*Note: equivalence volume (Ve) is volume at which the acid and base are in equilibrium. The dilution formula can be used to solve for Ve.
Since we have started titrating with strong base, the weak acid is going to react with the strong base creating water and strong acid. We do not know the concentration of the strong acid, the ice table is used. The ice table will look as following
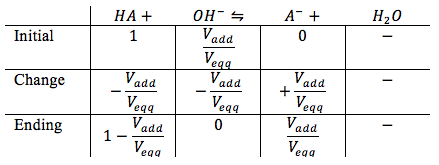
*Note: We ignore the concentration of water since it does not contribute to the pH. We are also assuming that since this is before the equivalence point there is more weak acid in the solution than strong base, thus weak acid is 1.
The pH equation is
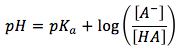
We can then plug in the concentrations from the ice table, the pH equation then looks as following
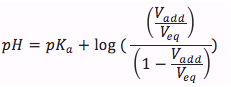
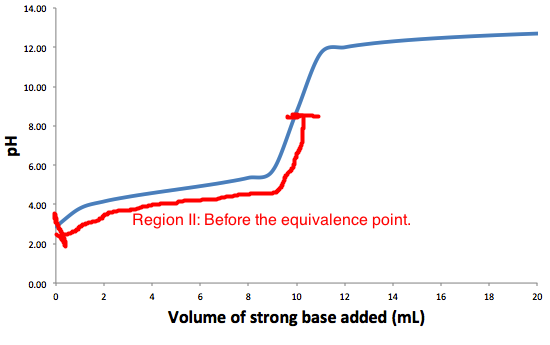
The graph represents a typical titration graph of a weak acid with strong base, with region II highlighted in red.
Description
The equation is
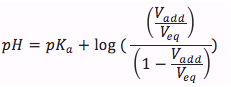
where
- Vadd is the volume added of the strong acid in units of (mL)
- Veq is the equivalence volume in units of (mL)
- pKa is the log of acid equilibrium constant, can be found here.
References
Harris, 9th Edition. Pp.236-238
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
