V2 - Vector addition orthogonal vectors (magnitude)
Tags | |
UUID | 77892424-0ba1-11e4-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
This equation computes the sum of two orthogonal vectors.
This is one of the simplest ways to show vector addition since one vector is purely in the y-direction and the other vector is in the x-direction. See Vector addition by components to see vector addition of two vectors show have both x and y components.
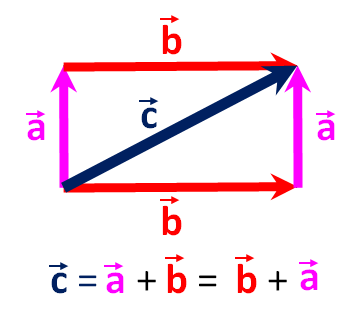
Note that to simplify the graphical example and the explanation of vector addition, we show vector begins at the origin of the Cartesian axes and so vector points in they-direction. Nevertheless, we know that vectors are defined by their length and direction and can thus occur anywhere on the X/Y plane and still be the same vectors. That principle of vectors is also why you can add to by placing the tail of at the head of and get the same resultant vector as when you add to by placing the tail of at the head of .
Notes
A vector is a mathematical concept of an object that has direction and length. A line alone is not a vector but a line with orientation spanning the distance between two points in space is a vector.
The graphic shows that = + = +
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
