Ionic strength
Tags | |
UUID | 8b0d9f42-2e97-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Ionic strength calculator computes ionic strength based on the .
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (c1) Molar concentration of species 1
- (z1) Charge of species 1
- (c2) Molar concentration of species 2
- (z2) Charge of species 2
- (c3) Molar concentration of species 3
- (z3) Charge of species 3
Ionic strength (I): The strength of concentration is returned in moles per liter (mol/L). However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
Ionic strength (for the Spanish site click here) expresses the concentrations of all electrolytes in an aqueous solution based on their molarity and charge.1 This parameter impacts the solubility of salts in water. Increasing ionic strength allows more salt to dissolve into the solution.
The equation for Ionic Strength is:
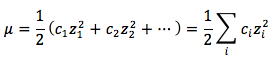
where
- μ is the Ionic Strength
- ci is the molar concentration of the ith species in units of (mol/L)
- zi is the charge of the ith species.2
Ionic strength can also be calculated using molality instead of molarity3 since in non-ideal solutions, volumes are not necessarily additive.
References
1. Williams, V.R., W.L. Mattice, and H.B. Williams, Basic Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences, 3rd Ed., W. H. Freeman, (1978).
2. Harris, D., Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 9th Ed., W. H. Freeman, Pp.163 (2015).
3.IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1997). XML on-line corrected version: http://goldbook.iupac.org (2006-) created by M. Nic, J. Jirat, B. Kosata; updates compiled by A. Jenkins. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8. doi:10.1351/goldbook. Last update: 2014-02-24; version: 2.3.3.DOI of this term: doi:10.1351/goldbook.I03180.
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
