Stress (Tangential) out Cylinder
Tags | |
UUID | a63dac7f-b61d-11e4-a9fb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Stress (Tangential) out Cylinder calculator computes the tangential stress on the outer wall of a closed cylindrical vessel.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (P) Pressure Outside of Closed Cylinder
- (ro) Outer Radius of Cylinder
- (ri) Inner Radius of Cylinder
Stress (Tangential) out Cylinder (σext): The results are returned in units of Newtons per meter squared.. However, these can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
This equation for stress computes the tangential stress (σt) on the outer wall of a closed cylindrical pressure vessel.1 The tangential stress is also sometimes called the "hoop stress" as it is the surface wall stress all the way around the circumference of the cylinder. The pressure inside the vessel for this equation is assumed to Pi = 0.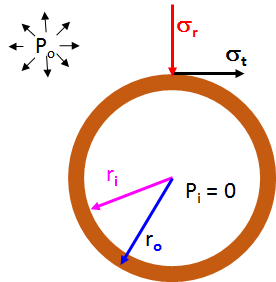
The Tangential Stress outside a Cylinder calculator computes the tangential stress on the inner wall of a closed cylindrical pressure vessel.1 The tangential stress is also sometimes called the "hoop stress" as it is the surface wall stress all the way around the cylinder. The formula for the Tangential Stress in a Cylinder is:
σt_ext=-P⋅r2o+r2ir2o - r2i
where:
- σext = Tangential Stress in a Cylinder
- P = the pressure outside the closed cylinder
- ro = outer radius of the cylinder
- ri = inner radius of the cylinder
Cylinder Stress Calculators
- Stress (Radial) in Cylinder
- Stress (Tangential) in Cylinder
- Stress (Radial) out Cylinder
- Stress (Axial) in Cylinder

Cylinder Calculators
- Cylinder Side Area: Computes the surface area of the sides of a cylinder based on height and radius.
- Cylinder Surface Area: Computes the total surface area of a cylinder including sides, top and bottom.
- Cylinder Volume: Computes the volume of a cylinder based on cylinder height and radius.
- Cylinder Volume from Height and Circumference: Computes the volume of a cylinder based on the height and circumference. It also returns the diameter of the cylinder.
- Cylinder Height: Computes the height of a cylinder based on the volume and radius.
- Cylinder Radius: Computes the radius and diameter of a cylinder based on the volume and height.
- Cylinder Weight: Computes the weight, mass and volume of a cylinder based on the height, radius and density.
- Cylinder Mass Computes the mass of a cylinder based on the radius and height and mean density of the cylinder.
- Volume in Horizontal Cylinder: Computes partial volume of a horizontal circular cylinder based on the radius and length of the cylinder and the vertical height of the contents in the cylinder (see diagram).
- Cylinder Density: Computes the mean density of a cylinder based on the mass and computed volume from the radius and height.
- Slanted Cylinder Surface Area: Computes the surface area of a slanted cylinder based on the radius and side length (L).
- Slanted Cylinder Area from Angle: Computes the lateral area (surface area of the sides) of a slanted cylinder based on its radius, height and slant angle (θ).
- Slanted Cylinder Volume: Computes the volume of a slanted cylinder based on the radius of the base, side length and slant angle.
- Slanted Cylinder Weight: Computes the weight or mass of a slanted cylinder based on the radius, side length, slant angle and density.
- Cylinder MoI about Central Axis: Computes the moment of inertia of a cylinder about its central axis based on the mass and radius.
- Cylinder MoI about the End: Computes the moment of inertia of a solid circular cylinder of uniform density about an axis along the diameter of the cylinder at one end.
- Cylinder MoI Perpendicular to Axis: Computes the moment of inertia of a solid circular cylinder of uniform density about an axis perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder and through the center of mass.
- ^ Fundamentals of Engineering. 8th edition, 2nd Revision. National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES) - 2001. ISBN 978-1-932613-59-9. pg 33
Calculators
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
