Rate of Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator
Tags | |
UUID | baf4eb06-d520-11eb-8eb2-bc764e203090 |
The Rate of Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator finds the rate at which heat energy is transferred from one material to another.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (k) Thermal Conductivity (Wm-1K-1)
- (A) Area of Intersection
- (T1) Temperature 1
- (T2) Temperature 2
- (d) Thickness of Material
- (t) Time required to go from T1 to T2.
Rate of Conductive Heat Transfer (Q/t): The calculator returns the answer in Watts per minute. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
Conduction is the passing of heat energy between two objects in direct contact. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. A higher temperature results from fast-moving molecules. Lower temperatures results from slow-moving molecules. When a low and high temperature object come in direct contact, their molecules interact. The fast-moving molecules spread heat from the higher temperature object to the lower temperature object until they both reach the same temperature.
Some materials are greater conductors than others. Conduction happens depends on several factors:
- Material the objects are made from (their conductivities)
- Surface area of the two objects in contact
- Difference in temperature between the two objects
- Thicknesses of the two objects
To find the rate of conductive heat transfer, use the formula: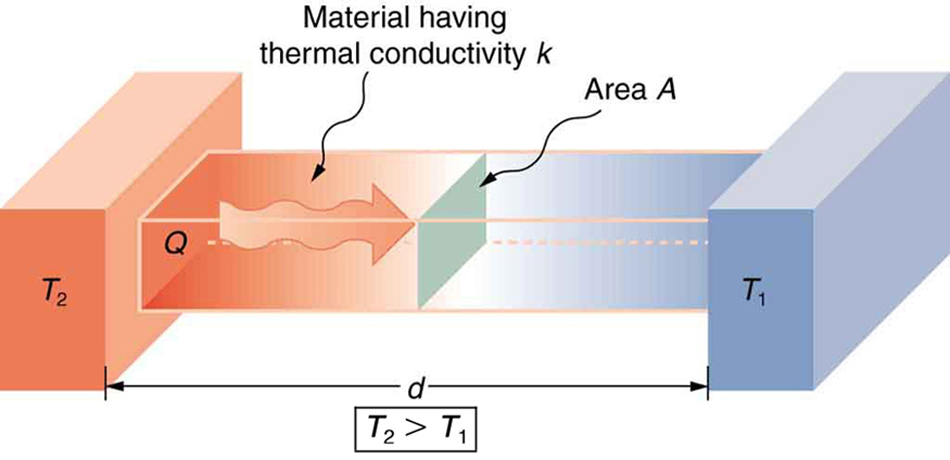
` Q / t = [ kA ( T2 - T1 ) ] / d `
where:
Q / t = rate of heat transfer
k = thermal conductivity of the material
A = surface area of contact between the two objects
T1 = temperature of one object
T2 = temperature of the other object
d = thickness of the material
References
Heat Transfer Through Conduction: Equation & Examples (https://study.com/academy/lesson/heat-transfer-through-conduction-equation-examples.html#:~:text=The%20equation%20for%20conduction%20tells,%2D%20T1)%2C%20divided%20by%20the)
OpenStax College Physics (https://openstax.org/books/college-physics/pages/14-5-conduction)
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
