Quonset Hut Coating Amount
Tags | |
UUID | bc2bef4b-b5fb-11ee-a8f1-bc764e203090 |
The Quonset Hut Coating Amount calculator computes the exterior surface area (A) of a Quonset hut based on the height, length, width, corrugation factor, and thickness of coating. This includes the roof and both ends. See YouTube instruction video for this formula HERE.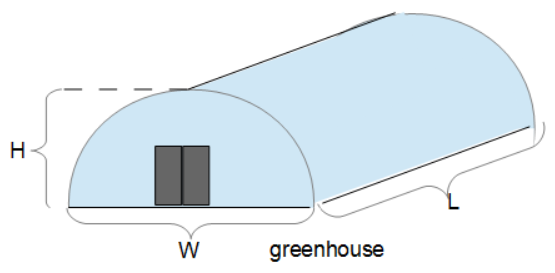
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (L) Length of Quonset Hut
- (H) Height of Quonset Hut
- (W) Width of Quonset Hut
- (cF) Corrugation Factor
- (t) Thickness of Coating
Quonset Hut Coating (QHC): The calculator returns the following:
- (SA) Smooth Surface Area of Quonset Hut
- (cSA) Corrugated Surface Area of Quonset Hut. This takes into account the corrugation.
- (v) Volume of Coating Material
The above can be automatically converted into compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The calculator assumes that the face of the Quonset hut is half of an ellipse (or circle if W = 2*H). From that, the tally of the total surface area gets pretty easy using the formulas for the Area of an Ellipse, and the Circumference of an Ellipse.
The formula for the area of an ellipse is:
A = π•a•b
The circumference of an ellipse has been approximated in several simple formulae including this one by the famous mathematician Rumanujan. The the formula for the circumference of an ellipse used in this calculator is:
C=π⋅[3⋅(a+b)−√(3⋅a+b)(a+3⋅b)]
where:
- C = circumference of ellipse
- a = length of semi-major axis (W/2 in our example)
- b = length of semi-minor axis (H in our example)
Combining the two formulas, the Surface Area of a Quonset Hut is:
SA = A + C/2*L
where:
- SA = Surface Area of the Quonset Huthttps://www.vcalc.com/wiki/quonset-hut-surface-area
- A = Area of the ellipse (half on either side of the Quonset Hut)
- C = Circumference of the ellipse
- L = Length of the Quonset Hut
The surface area of a Quonset Hut is useful for calculating construction material needs and for computing the conductive heat loss of the Quonset hut.
Quonset Hut Calculators
- A = Area of the Ellipse
- b = length of the semi-minor axis
- a = length of the semi-major axis
Corrugation
Corrugation refers to the process of shaping a material into a series of parallel ridges and grooves. This is commonly seen in corrugated materials, such as cardboard or metal sheets. The purpose of corrugation is often to add strength and rigidity to the material while maintaining flexibility. In the case of corrugated cardboard, for example, the corrugated structure provides strength and helps the material withstand pressure and impacts. Corrugated metal sheets are used in roofing and packaging for similar reasons.
Corrugation adds complexity to the basic surface area calculation. Without corrugation the surface area of a rectangle can be calculated as length time width. To account for corrugation, and in essence flatten the surface area calculation, one can use a Corrugation Factor (CF) that can by applied to a dimension (e.g., width) in order to make an accurate surface area of a corrugated surface calculation.
Corrugation can have a smooth (curved) or straight segment pattern with squared ends in its profile.
Corrugation Factor
Surface area is a simple length times width calculation, but what if one of the dimensions is not smooth? This is found in corrugated material. To account for this, this calculator has a corrugation factor that is applied to the length and width dimensions to account for corrugation.
Straight (Squared) Corrugation Profile
Curved Corrugation Profile:
Corrugation refers to the process of shaping a material into a series of parallel ridges and grooves. This is commonly seen in corrugated materials, such as cardboard or metal sheets. The purpose of corrugation is often to add strength and rigidity to the material while maintaining flexibility. In the case of corrugated cardboard, for example, the corrugated structure provides strength and helps the material withstand pressure and impacts. Corrugated metal sheets are used in roofing and packaging for similar reasons.
To calculate the Corrugation Factor, do the following:
- Measure the linear Width (W in the diagram above), for any length of the corrugation.
- Use a string, and lay it on top of the same length, letting is fall into all the recesses as much as possible.
- Mark the end of the string to match the end of the Width.
- Pull the string straight and measure how much longer it is than the Width.
The formula for the Corrugation Factor is:
CF = SL / W
where:
- CF = Corrugation Factor
- SL = String Length
- W = Width of Corrugated Segment
Shout Out
Special thanks to Travis Barnett from Wyoming Insulation and his math teacher cousin Brad for the inspiration for this calculator.
Equations and Data Items
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

