Model Rocket Altitude
Tags | |
UUID | e3f52e14-6564-11e4-a9fb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Model Rocket Altitude calculator computes the estimated maximum altitude of a rocket based the distance from the launch point and the angle to top point of flight (zenith).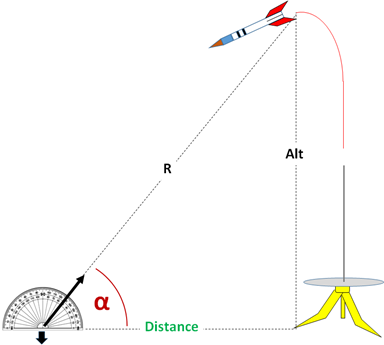
INSTRUCTION: Choose units and enter the following:
- (D) Distance to Spotter (from launch to spotter)
- (α) Angle of Max Height (from horizon to apex or zenith of flight)
Max Altitude (Alt): The calculator returns the observed altitude in feet. However this can be automatically converted to other distance units (e.g. meters) via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
Note this calculation makes a gross assumption that the rocket flight's apex is directly over the launch point, which in most model rocket flights is a reasonable approximation. The Model Rocket Altitude equation estimates the maximum altitude a rocket will achieve using the distance a spotter is from the launch pad and the angle from the ground the spotter notes at the rocket's apex. This altitude estimate is most accurate if the rocket flies straight up, perfectly vertical from the launch pad.
The Model Rocket Altitude equation can estimate the altitude of a rocket at any point in the rocket's flight path where the angle is measured. It does this by multiplying the distance from the launch pad by the tangent of the angle of the rocket's apex (See Figure 1). This equation is based on the Pythagorean Theorem1. The Pythagorean Theorem defines the relationship between the three sides of a right triangle; to calculate the altitude of a rocket using the Pythagorean Theorem the following must conditions need to be met:
- the distance from the spotter to a point directly beneath the rocket at its apex must be known and level
- the rocket must launch vertically from the launch pad
If both of these conditions are met, the vertical flight path forms a right angle with the ground level and the calculation of apex altitude can be done.
Using the trigonometric functions of a right triangle2 the Altitude can be found by multiplying the angle, , by the Distance of the spotter from the launch vertical.
 Free Fall Calculators
Free Fall Calculators
- Free Fall (time): Computes the duration of time that an object will be in free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (distance): Computes the distance that an object will be in free fall based on the duration of the fall and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Velocity at Impact): Computes the final velocity of an object after a free fall based on the height and the acceleration due to gravity.
- Free Fall (Energy on Impact): Computes the kinetic energy at impact based on the height of free fall, acceleration due to gravity and the mass of the object.
- Model Rocket Altitude: Computes the estimated maximum altitude of a rocket based the distance from the launch point and the angle to top point of flight (zenith).
- Object Height by Time to Drop: Estimates the height of an object based on the time it takes for an object to drop from the top of it.
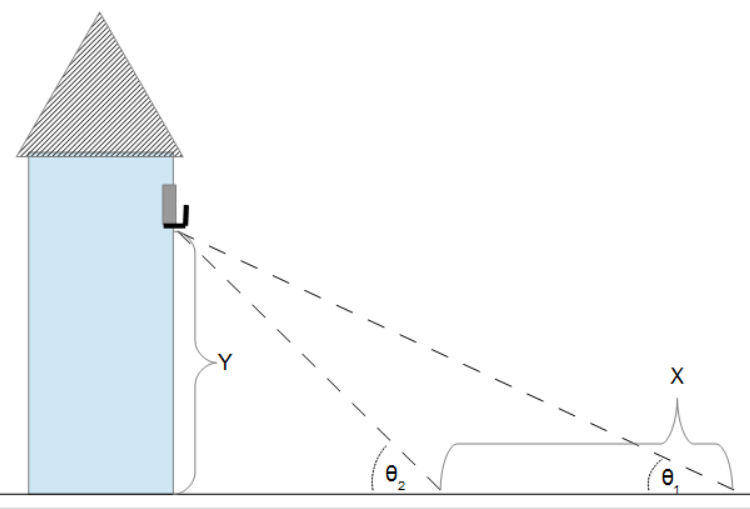
- Elevation of Object (angles and separation): Computes the height of an object based on two angle measurements and the distance between them.
- Distance Traveled at Constant Acceleration: Computes the distance traveled by an object after a period of time, based on its initial distance from the origin, initial velocity and a constant acceleration.
- g (acceleration due to gravity at sea level): Acceleration due to Gravity (g) at sea level on Earth is 9.80665 m/s2.
- Height Calculated from Time of Fall
- Ballistic Maximum Altitude: This is the maximum altitude achieved in free ballistic flight.
- Ballistic Maximum Range: This is the maximum horizontal range.
- Ballistic Flight Time: This is the time duration of free flight.
- Ballistic Position: This computes the X,Y position at a given time.
- Ballistic Vertical Velocity: This is the vertical velocity at a given time.
- Ballistic Horizontal Velocity: This is horizontal velocity or ground speed.
- Vertical Position in Ballistic Flight: This compute the vertical position (y) at a given time within ballistic flight.
- Horizontal Position in Ballistic Flight: This compute the horizontal position (x) at a given time within ballistic flight.
- Velocity to achieve a Max Ballistic Height: This computes the initial velocity required to achieve the max height.
Practical Application
The following steps can be used to construct a homemade altitude finder to measure the apex angle.
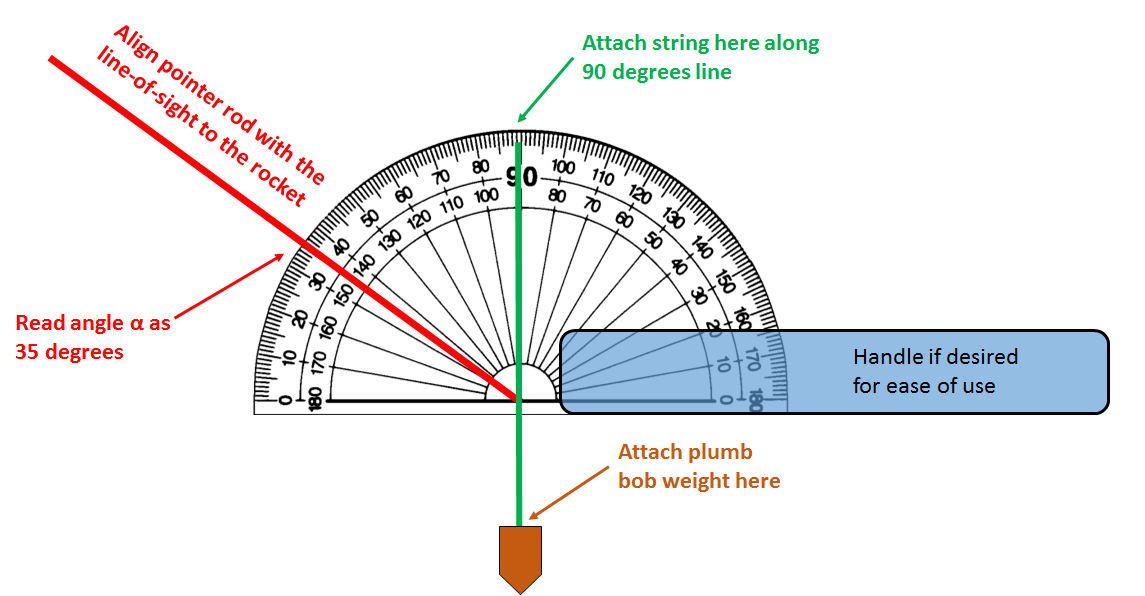 Figure 2
Figure 2
The following supplies will be needed:
- a standard transparent protractor
- a straight rod (e.g. the straight segment of coat hanger or thin dowel)
- a string with a weight attached at one end (e.g. a heavy washer)
Steps
- Attach the string near the top of the 90 degree line and allow the weight to hang down
- Attach the rod to the pivot point of the protractor so that the rod can rotate (on the opposite side from the string hanging down).
- While holding the protractor so that the string aligns with the 90 degree line, sight along the rod to the rocket at its apex. When the string aligns with 90 degrees, the base of the protractor is parallel to the Earth's surface and forms the 90 degree angle with the vertical at the launch pad.
- Read the angle of the rod against the protractor; this is angle
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

