The Renal Blood Flow calculatore computes the renal blood flow, RBF, from the renal plasma flow and the volume percentage or red blood cells (the hematocrit). 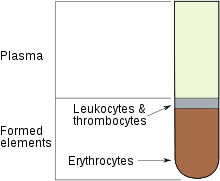 hematocrit
hematocrit
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (RPF) This is the renal plasma flow
- (HCT) This is the hematrocrit percentage, also known as the packed cell volume (PCV) and the erythrocyte volume fraction (EVF)
Renal Blood Flow: The calculator returns the RBF in liters per minute (L/m). However, this can be automatically converted to other volumetric flow units (e.g. mL/s) via the pull-down menu.
Renal Blood Flow
The Renal Blood Flow equation computes the RBF based on the plasma flow rate (RPF) and the volume (%) of red blood cell. Inputs to this equation are:
- RPF - the renal plasma flow
- HCT - the hematrocrit, also known as the packed cell volume (PCV) and the erythrocyte volume fraction (EVF)
In the physiology of the kidney, renal blood flow (RBF) is the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time. In humans, the kidneys together receive roughly 22% of cardiac output, amounting to 1.1 L/min in a 70-kg adult male. RBF is closely related to renal plasma flow (RPF), which is the volume of blood plasma delivered to the kidneys per unit time.
While the terms generally apply to arterial blood delivered to the kidneys, both RBF and RPF can be used to quantify the volume of venous blood exiting the kidneys per unit time. In this context, the terms are commonly given subscripts to refer to arterial or venous blood or plasma flow, as in RBFa, RBFv, RPFa, and RPFv. Physiologically, however, the differences in these values are negligible so that arterial flow and venous flow are often assumed equal.
Hematrocrit
The hematocrit (Ht or HCT, British English spelling haematocrit), also known as packed cell volume (PCV) or erythrocyte volume fraction (EVF), is the volume percentage (%) of red blood cells in blood. It is normally 45% for men and 40% for women. It is considered an integral part of a person's complete blood count results, along with hemoglobin concentration, white blood cell count, and platelet count. Anemia refers to an abnormally low hematocrit, as opposed to polycythemia, which refers to an abnormally high hematocrit. Both are potentially life-threatening disorders.
See Also
- Body Surface Area - Medical calculator for BSA with different algorithm, units and demographic means
References
- Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hematocrit
- Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renal_blood_flow