Tags | |
Hypotenuse - Pythagorean Theorem
This equation uses the Pythagorean Theorem to compute the length of one of the sides of a right triangle given inputs of the length of the other side and the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
Description
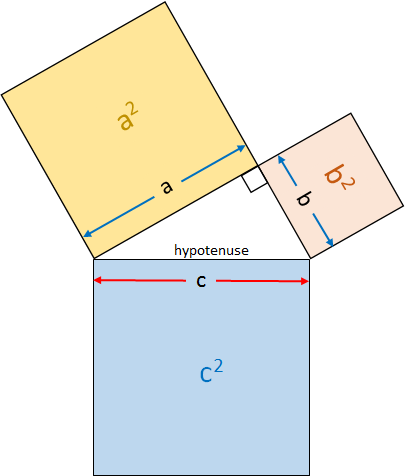
The Pythagorean Theorem is shown graphically in the picture. The sum of the area of the two squares whose sides are a and b (as shown in the picture) is equal to the area of the square whose side is equal to c. In this picture the hypotenuse of the right triangle whose sides are formed by one edge of each of the three squares is of length c.
In other words, this picture graphically portrays the Pythagorean Theorem:
Proof
There are hundreds of existing proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem. The Guinness Book of Records records that there are 367 such proofs but those do not include a number that are unpublished and which may include even mechanical proofs.
See Also
Pythagorean Theorem [multiple proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem]

