Processing...
`s = sqrt( "r" ^2 - 2* "r" * "R" * cos( theta ) + R^2`
Enter a value for all fields
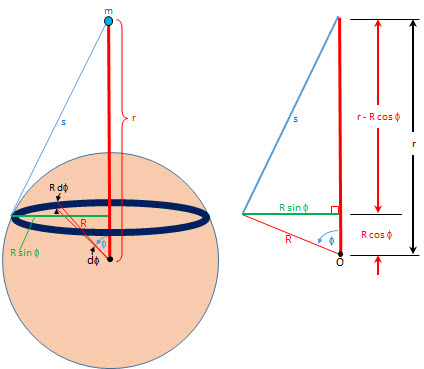
if we have a point, m, (as in the picture), somewhere on an axis that extends outside a sphere, we can compute the distance, s, from that point to any point on the sphere by first realizing the perpendicular line to the axis that passes through the point on the sphere forms a right triangle and the distance, s, is the hypotenuse of that right triangle. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can compute the distance, s, from the following inputs:
- r - the distance between the point, m, and the center of the sphere (remember, point m can be inside the sphere)
- R - the radius of the sphere
- `theta` - the angle between the axis through the point, m, and the radial line through the point on the sphere
The output is length s
Notes
s is the hypotenuse of the right triangle with the sides: (r - R * cos(`theta`) and R * sin(`theta`)