Tags | |
UUID | 6548a406-d011-11e4-a3bb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Continuity Equation (Velocity) calculator computes the initial velocity in a pipe (V1) using the continuity equation based on the initial fluid density and cross-section area and the final fluid density, velocity and cross-section area.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following: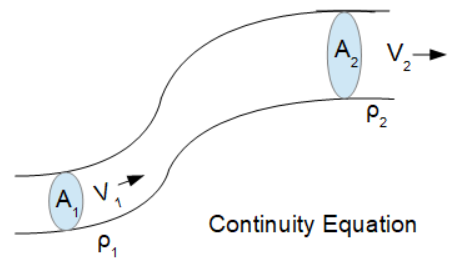
- (ρ1) This is the initial fluid density
- (A1) This is the initial cross-section area
- (A2) This is the final cross-section area
- (ρ2) This is the final fluid density
- (V2) This is the final fluid velocity
Continuity Equation for Velocity (V1): The calculator returns the area in meters per second. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
Related Calculators:
- Continuity Equation (Density)
- Continuity Equation (Velocity)
- Continuity Equation (Area)
- Bernoulli's Pressure
- Bernoulli's Velocity
- Bernoulli's Elevation
The Math / Science
The Continuity Equation states that the product of fluid density (ρ), fluid velocity (V), and cross-section area remains constant in a closed system. In this way, you can use the Continuity Equation to compute one of the parameters for two places in the system if the remain parameters are known. Mathematically, the Continuity Equation is:
A1 • ρ1 • V1 = A2 • ρ2 • V2
where:
- A1 is the initial cross-section area
- ρ1 is the initial fluid density
- V1 is the initial fluid velocity
- A2 is the final cross-section area
- ρ2 is the final fluid density
- V2 is the final fluid velocity
Reference
Young, Hugh and Freeman, Roger. University Physics With Modern Physics. Addison-Wesley, 2008. 12th Edition, (ISBN-13: 978-0321500625 ISBN-10: 0321500628 ) Pg 467, eq 14.12
Calculators
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
