Tags | |
UUID | 1a0e9666-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Example 1
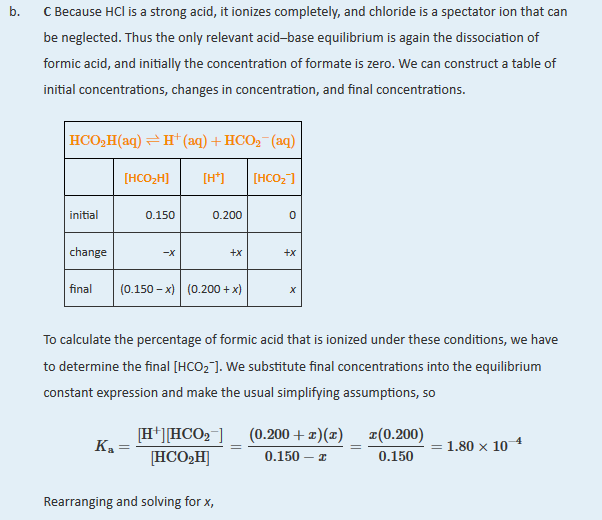
| I am not recording a livescribe for this problem as it follows closely previous problems. Solution: A Because sodium formate is a strong electrolyte, it ionizes completely in solution to give formate and sodium ions. The Na+ ions are spectator ions, so they can be ignored in the equilibrium equation. Because water is both a much weaker acid than formic acid and a much weaker base than formate, the acid–base properties of the solution are determined solely by the formic acid ionization equilibrium: 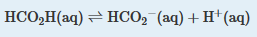
The initial concentrations, the changes in concentration that occur as equilibrium is reached, and the final concentrations can be tabulated.
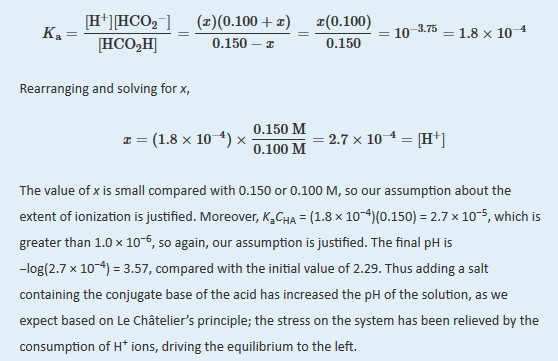
B We substitute the expressions for the final concentrations into the equilibrium constant expression and make our usual simplifying assumptions, so
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Calculators and Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.