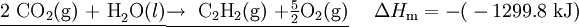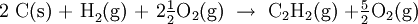Tags | |
UUID | 19ba3a5f-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Example 10
|
See the calculation on this YouTube video Solution We use the following strategy to manipulate the three experimental equations so that when added they yield Eq. (1): a) Since Eq. (1) has 2 mol C on the left, we multiply Eq. (2a) by 2. b) Since Eq. (1) has 1 mol H2 on the left, we leave Eq. (2b) unchanged. c) Since Eq. (1) has 1 mol C2H2 on the right, whereas there is 1 mol C2H2 on the left of Eq. (2c) we write Eq. (2c) in reverse. We then have
?Hm = (-787.0 -285.8 + 1299.8) kJ =227.0 kJ Cancelling 5/2 O2 on each side, the desired result is 2C(s) + H2(g) ? C2H2(g) ?Hm = 227.0 kJ |
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.