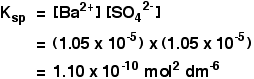Tags | |
UUID | 19f73a7a-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
The Common Ion Effect
From UCDavis Chemwiki
|
This page was also found in Chapter 19, but is pertinent here so is included in this chapter as well. Le Châtelier's Principle states that if an equilibrium gets out of balance, the reaction will shift to restore the balance. If a common ion is added to a weak acid or weak base equilibrium, then the equilibrium will shift towards the reactants, in this case the weak acid or base. IntroductionThe common-ion effect is used to describe the effect on an equilibrium involving a substance that adds an ion that is a part of the equilibrium.
A Simple ExampleSuppose you tried to dissolve some lead(II) chloride in some 0.100M sodium chloride solution instead of in water. What would the concentration of the lead(II) ions be this time? As before, let's call the concentration of the lead(II) ions s.
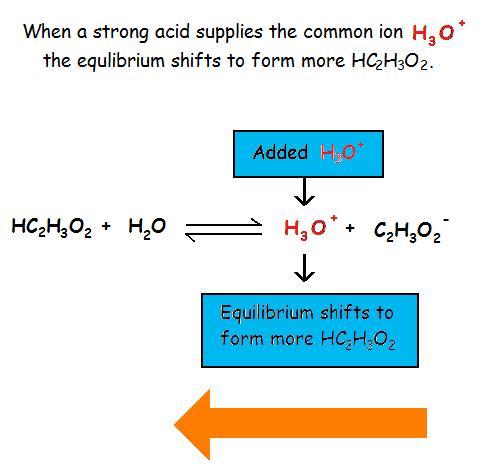
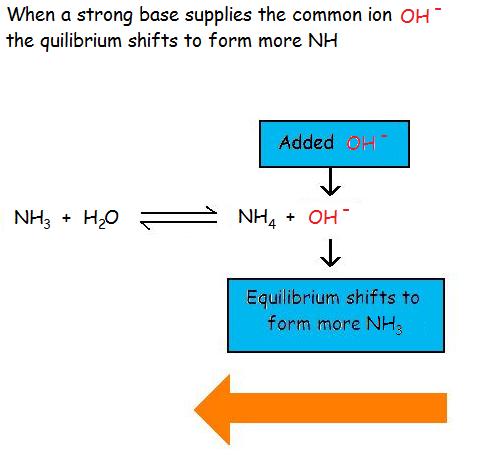
Common Ion Effect on Weak Acids and BasesAdding a common ion prevents the weak acid or weak base from ionizing as much as it would without the added common ion. The common ion effect suppresses the ionization of a weak acid by adding more of an ion that is a product of this equilibrium.
|
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |