The Fraction of Dissociation calculator compute the fraction of weak-acid that dissociates in a solution based on the formal concentration (F) and the concentration of [A-].
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the preferred units and enter the following:
- (F) This is the formal concentration.
- (x) This is the concentration of [A-].
Fraction of Dissociation(α): The calculator returns the fraction of dissociation as a real number. However, this can be automatically converted to a percentage via the pull-down menu.
General Information
The fraction of dissociation of an acid calculates the fraction of weak-acid that dissociates in a solution and is used in weak-acid calculations.
How a weak-acid problem is solved:
Supposed you have a typical acid dissociation reaction equation and you are asked to solve for the pH of the weak-acid.The typical acid dissociation reaction is
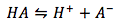 with its equilibrium expression
with its equilibrium expression 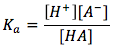
Since the acid dissociates in a solution, thus there will also be a water equilibrium equation
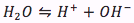 with its equilibrium expression
with its equilibrium expression 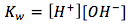
We can also use the mass balance and charge balance equations to help us solve for the unknowns.
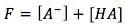 (mass balance)
(mass balance)
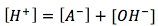 (charge balance)
(charge balance)
Using these equations we can find the pH, but first we must make some assumptions. [A-] and [H+] is produced when weak acid dissociates. When water dissociates, [OH-] and [H+] are produced. When more HA is dissociated in solution than water, we can assume that the concentration of [A-] is far greater than that of [OH-], so we can exclude [OH-]. Thus the charge balance equation becomes [H+]=[A-]. We can plug this in to the above equilibrium expression. We get the equation for the weak acids 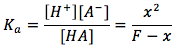 . By rearranging variables we can solve for x which is also [A-]=[H+] and plug that in to the pH equation.
. By rearranging variables we can solve for x which is also [A-]=[H+] and plug that in to the pH equation.
Description
The equation is
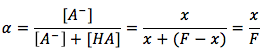
where
- x is the concentration of the dissociated acid particle [A-] in units of (mol/L).
- F is the formal concentration in units of (mol/L).
- Alpha is the fraction of [A-] dissociated in the solution.
Related Topics
- Mass balance (for the Spanish site click here)
- Charge balance (for the Spanish site click here)
- Equation for the weak acid (for the Spanish site click here)
- Acid equilibrium constant (for the Spanish site click here)
References
Harris, 9th Edition. Pp.193