Poiseuille's Law
Tags | |
UUID | e6700a88-ed9f-11e3-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
The Poiseuille's Law calculator computes the flow rate in a pipe based on the change of pressure, the length of pipe, the inner radius and the viscosity of fluid.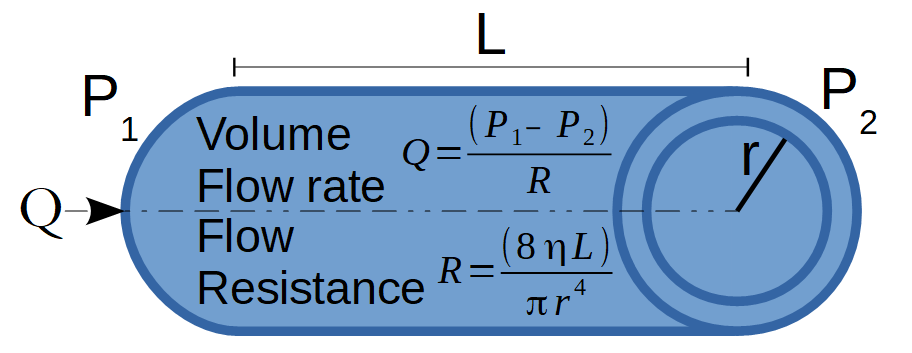
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (P1) Initial Pressure
- (P2) Final Pressure
- (r) Inner Radius of Pipe
- (L) Length of Pipe
- (η) Viscosity of Fluid
Poiseuille's Law Flow Rate (Q): The calculator returns the flow rate in milliliters per minute (mL/min). However, the can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
Related Calculators
- Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance
- Poiseuille's Law
- Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids
- Compute the Heart Chamber Pressure via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Heart Wall Stress via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Blood Flow Rate using Darcy's Law
- Compute the Change in Vascular Pressure
- Compute Blood Pressure
The Math / Science
The relationship between pressure and continuous laminar flow of fluid in a rigid tube is described by Poiseuille's law, which states that the flow rate of a fluid, Q, is directly proportional to the pressure difference, along the length of the tube and the fourth power of the radius of the tube, and inversely proportional to the tube length, and fluid viscosity. The formula for Poiseuille's Law is:
`Q = ((P_1 - P_2) πr^4)/(8Lη)`
where:
- Q is the volume flow rate
- P1 is the initial pressure
- P2 is the final pressure
- r is the inner radius
- L is the length
- η is the viscosity of fluid
To see the derivation of this formula, watch this following YouTube video: https://youtu.be/cVdJh8kI6Sw
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
