CHM1 16 Gibbs Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant Collectio
Tags | |
UUID | 19e48d21-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
Gibbs Free Energy and the Equilibrium Constant
From UCDavis Chemwiki
`DeltaG`: Gibbs Free Energy
`DeltaG` is the change of Gibbs (free) energy for a system and `DeltaG°` is the Gibbs energy change for a system under standard conditions (1 atm, 298K). On an energy diagram, `DeltaG` can be represented as:
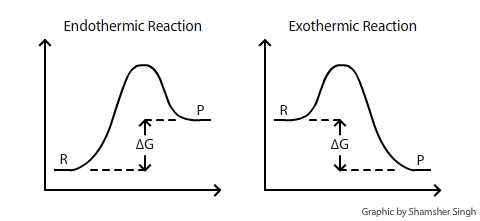
Where `DeltaG` is the difference in the energy between reactants and products. In addition `DeltaG` is unaffected by external factors that change the kinetics of the reaction. For example if Ea(activation energy) were to decrease in the presence of a catalyst or the kinetic energy of molecules increases due to a rise in temperature, the `DeltaG` value would remain the same.
K: The Equilibrium Constant
K is the equilibrium constant of a reaction and is given by the reaction quotient:
`aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD`
`K = ([A]^a [B]^b)/([C]^c [D]^d)`
The connection between Gibbs free energy and constant equilibrium are directly related in the following equation:
- `R = 8.314 J mol C^(-1)`
- `T = Temperature in K`
- `n = "moles of "e^(-)" in a balanced redox reaction."`
- `F = "Faraday's Constant" = 96,485 C"/mol"`
These relationships are summarized as follows:
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0 | K | Product Formation |
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0 < 0` | K > 1 | Products favored over reactants at equilibrium. |
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0= 0` | K = 1 | At equilibrium when [C]c[D]d…= [A]a[B]b…(very rare) |
| `DeltaG_"rxn"^0 > 0` | K < 1 | Reactants favored over products at equilibrium |
This Collection is empty
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
