Iron Density
The mean density of iron is 7,847 kg/m3.
Weight of Iron Object Calculators
- Cylinder Weight: Weight of a cylinder based on dimensions and mean density.
- Sphere Weight: Weight of a sphere or ball based on radius of sphere and mean density.
- Ring Weight: Weight or a ring or gasket based on ring dimensions and mean density.
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe (from Latin: ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is one of the most abundant elements on Earth and is a crucial metal in various aspects of human civilization due to its strength, versatility, and abundance.
Iron is a transition metal and is found in several oxidation states in nature, with the most common being iron(II) and iron(III) compounds. It is typically silvery-gray in color and has a relatively high melting point.
One of the most notable uses of iron is in the production of steel. Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, with other elements often added to enhance its properties. Steel is widely used in construction, machinery, transportation, and many other industries due to its strength, durability, and versatility.
Iron also plays a vital role in biological systems, being an essential element for various biological processes, including oxygen transport in the blood (as part of hemoglobin and myoglobin), energy production, and enzymatic reactions.
Historically, iron has been used by humans for thousands of years, dating back to the Iron Age. It has been used for tools, weapons, and various other implements. The advent of ironworking revolutionized human societies, enabling the development of advanced civilizations.
Today, iron and its alloys are used in a wide range of applications, including construction, manufacturing, transportation (e.g., automobiles, ships, and railways), infrastructure, and consumer goods. Iron is also used in the production of various industrial chemicals and in the production of fertilizers.
Metals are materials characterized by its physical and chemical properties, primarily its ability to conduct electricity and heat, its luster or shine when polished, its malleability (ability to be hammered or pressed into shapes), and its ductility (ability to be drawn into wires). Metals typically have a crystalline structure and are found naturally in solid form (with the exception of mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature).
|
Metals Densities
|
Metals make up a large portion of the periodic table of elements, with examples including iron, copper, gold, silver, aluminum, and titanium, among many others. Metals are essential in various industries such as construction, manufacturing, electronics, transportation, and energy production due to their unique properties and versatility.
Metals are generally dense materials. Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume. Metals tend to have high densities because their atoms are closely packed together in a crystalline structure. This close packing of atoms contributes to their characteristic properties such as strength, malleability, and conductivity.
However, it's important to note that the density of metals can vary widely depending on factors such as their elemental composition, crystal structure, and any impurities present. For example, some metals like lead and platinum are denser than others like aluminum or magnesium.
The Weight of Metal Calculator contains functions and data to compute the weight (mass) of metal objects based on their size, shape and the density of the metal. The Weight of Metal functions are:
- Cylinder Weight: Computes the weight (mass) of a cylinder based on the radius, length (height) and density of metal.
- Sphere Mass: Computes the mass (weight) of a sphere based on the radius and density of metal.
- Hemisphere Mass: Computes the mass (weight) of a hemisphere based on the radius and density of metal.
- Weight of Metal Bars: Computes the mass (weight) of a number of metal flats or metal bars based on the dimensions and density of metal.
- Weight of Metal Rods: Computes the mass (weight) of a number of metal rods based on the dimensions and density of metal.
For the mean densities of other substances click HERE.
Weight or Mass of IRON Calculators: Use the mean density of iron (7,847 kg/m3) Iron Shaped Objects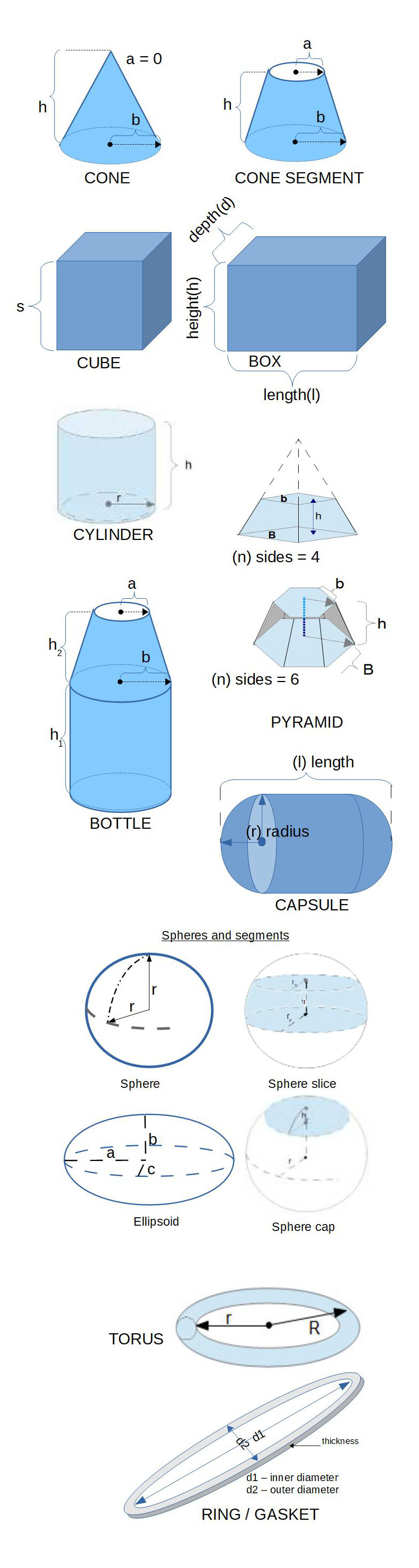 in any of the following formulas to compute the approximate mass or weight of the object made of iron based on its shape and dimensions.
in any of the following formulas to compute the approximate mass or weight of the object made of iron based on its shape and dimensions.
- To compute the weight or mass of ANY VOLUME of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a CUBE made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a BOX made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a PYRAMID made this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a PYRAMID SEGMENT made this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a CONE made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a CONE SEGMENT made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a CYLINDER made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a SPHERE made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a SPHERE SEGMENT made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a SPHERE CAP made of this material, CLLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a ELLIPSOID made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a PRISM made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a CAPSULE made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a TORUS made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a RING made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the weight or mass of a BOTTLE made of this material, CLICK HERE.
- To compute the time or cost to produce or consume a volume of material, see the Material Production Calculator.
- To compare the different prices in different volumes and different currencies, see the Material Purchasing Calculator.
- For the mean density of many substances, CLICK HERE.
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

