The Hyperboloid Volume calculator computes the volume of a single-sheet hyperboloid based on the dimensions.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (a) Formula Denominator a
- (c) Formula Denominator c
- (h) Height (length along perpendicular bisector)
Hyperboloid Volume (V): The surface area is returned in cubic meters. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The Hyperboloid Volume formula used in this calculator is for circular paraboloids and circular hyperboloids of one sheet. This is the case of surfaces of revolution. The circular hyperboloids have a=b which is why the inputs only have 'a' and 'c' and height h.
The Hyperboloid Volume equation computes the volume of a one-sheet hyperboloid. The formula for the volume of a one-sheet hyperboloid is:
`V = 1/3 pi h (2 a^2 + R^2) `
with `R = a*sqrt(1 + (h^2)/(4c^2))`
where:
- V = Volume of one-sheet hyperboloid
- c & a are parameter from the definition of the hyperboloid (see below)
- h = distance from apex along perpendicular bisector
A hyperboloid is a surface that may be obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of affine transformations. A hyperboloid is a quadric surface, meaning that it is defined by a polynomial equation of degree 2 in three variables.
There are different types of hyperboloids. The most common ones are: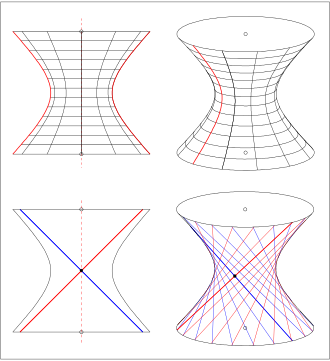
Hyperboloid of one sheet: This type of hyperboloid has two asymptotic cones and resembles two nested cones opening in opposite directions. Its equation in Cartesian coordinates is typically of the form:
` x^2 / a^2 + y^2/b^2 - z^2/c^2 = 1`
where a, b, and c are constants determining the shape and orientation of the hyperboloid along the three axes.
Hyperboloid of two sheets: This hyperboloid has two disconnected parts, each resembling a hyperboloid of one sheet. Its equation is similar to the hyperboloid of one sheet but with opposite signs:
` x^2 / a^2 + y^2/b^2 - z^2/c^2 = -1`
Hyperboloids find applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and architecture due to their interesting geometric properties and structural stability. For instance, they are used in the design of cooling towers, as well as in optics and acoustics.