The Solar Panel Calculator calculates the sunrise, sunset, solar elevation, and solar azimuth for a given date and location in 6-minute increments throughout the day.
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following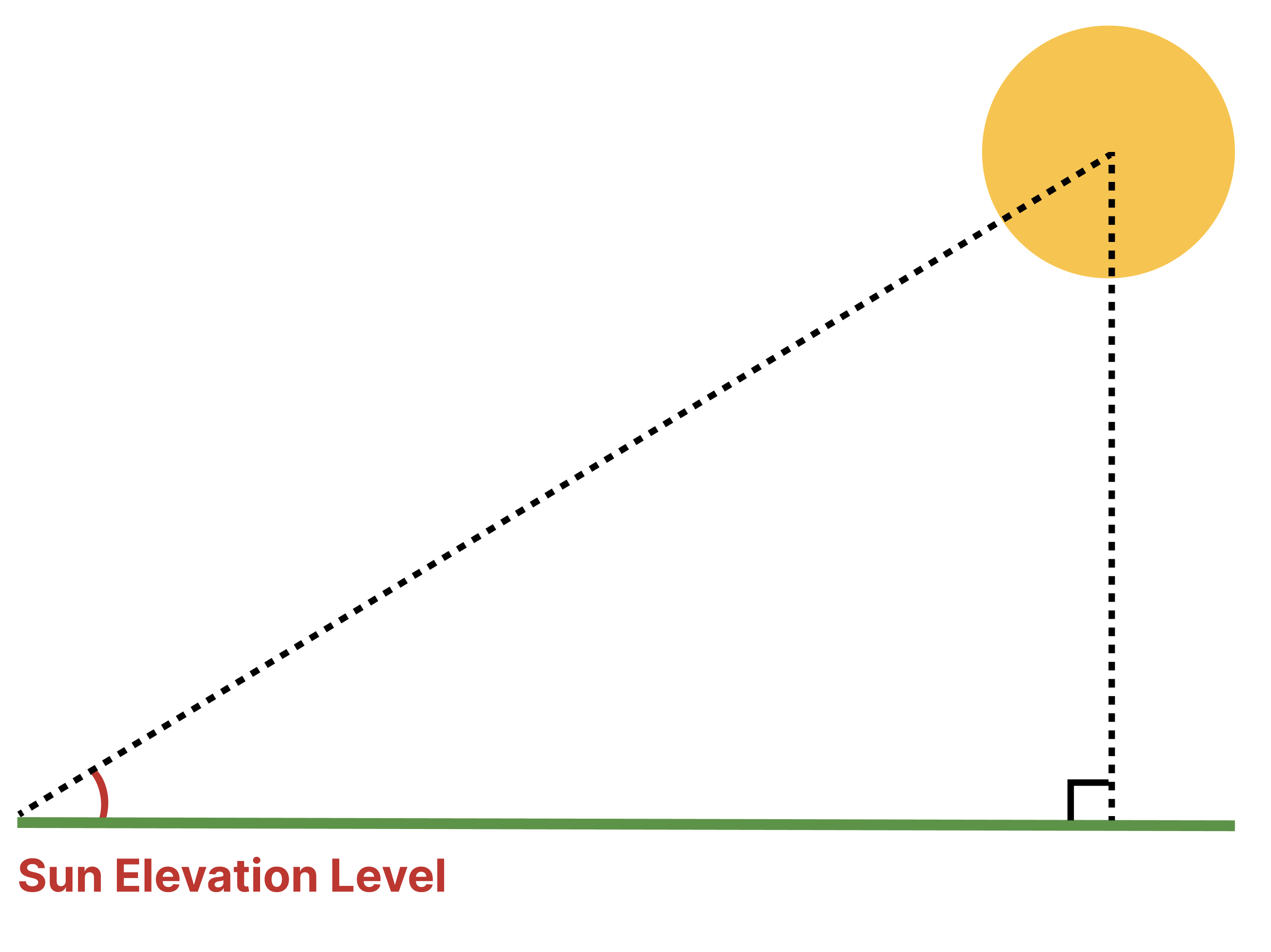
- (D) Date: Enter the desired date in mm/dd/yyyy format
- (Lat) Latitude: (+ to N) positive degree values are north of the equator
- (Long) Longitude: (+ to E) positive degree values are east of the Prime Meridian
- (TZ) Time Zone: (+ to E) positive hour increments are east of the Prime Meridian
- 0 = UTC
- (T) Time: Choose a time of day from the drop-down menu
Sunrise Time (SR): The sunrise time is returned in hh:mm:ss format
Sunset Time (SS): The sunset time is returned in hh:mm:ss format
Sun Elevation Angle (E): The sun elevation angle is returned in degrees
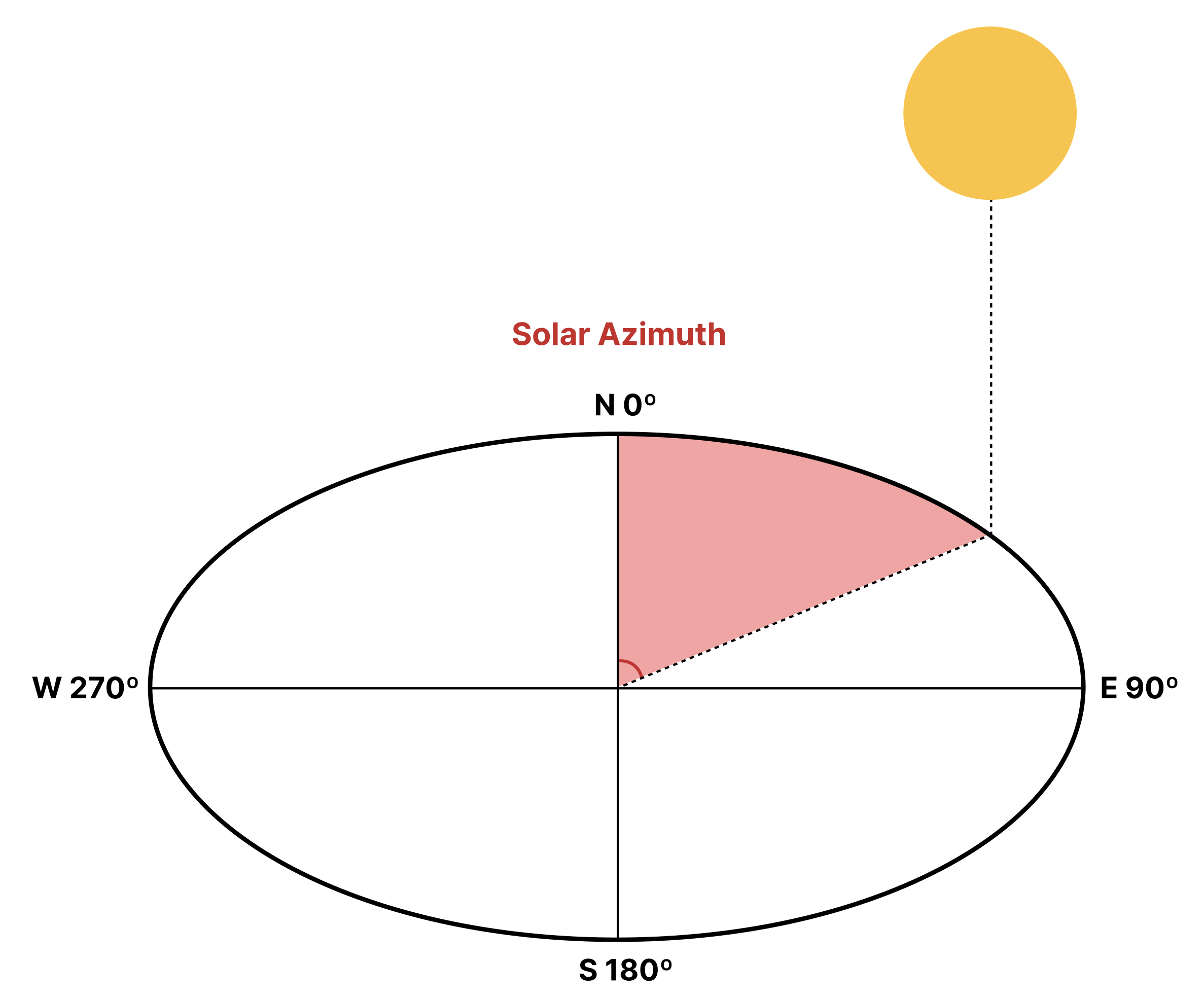
Solar Azimuth (A): The solar azimuth is returned in degrees
The Math / Science
- Sunrise time: the time when the sun's upper edge becomes visible above the horizon, marking the beginning of
 daylight. It varies daily due to Earth's tilt, orbit, and location, and is important for natural processes, astronomy, and planning activities.
daylight. It varies daily due to Earth's tilt, orbit, and location, and is important for natural processes, astronomy, and planning activities. - Sunset time: the moment when the sun's upper edge disappears below the horizon, signifying the end of daylight. It is influenced by celestial, geographic, and atmospheric factors and holds significance for agriculture, navigation, cultural events, and establishing reference points for celestial observations.
- Sun Elevation Angle: This refers to the vertical height of the sun above the observer's horizon. It is measured as the angle between the horizontal plane and the line drawn from the observer to the center of the sun. This angle changes throughout the day as the sun rises and falls, impacting the intensity of solar radiation received by a location and influencing the efficiency of solar panels and other solar energy systems.
- Solar Azimuth: Solar azimuth refers to the horizontal direction of the sun relative to an observer's position. It is measured as the angle between the observer's due north reference direction and the line drawn from the observer to the center of the sun projected onto the observer's horizontal plane. Solar azimuth is crucial in determining the optimal orientation of solar panels to maximize sunlight capture and energy production.
These terms provide critical information about the timing and positioning of the sun. Knowing the sunrise and sunset times helps in determining the duration of sunlight available for energy generation. Additionally, the sun's elevation angle and azimuth guide the proper orientation of solar panels, ensuring they are positioned optimally to receive maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day, leading to increased energy efficiency and production.