Terminal Velocity
Tags | |
UUID | 912d1a43-c544-11e5-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Terminal Velocity calculator computes the maximum velocity (Vt) that an object can achieve falling freely through the Earth's atmosphere based on the surface area (A), a drag coefficient (Cd), the density of the air (ρ), the mass of the object (m) and the acceleration due to gravity(g). Common Drag Coefficients 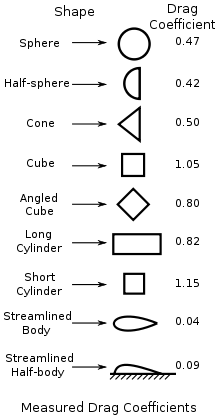
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (A) Surface area of falling object in the direction of motion.
- (Cd) Drag coefficient
- (ρ) Density of air
- (m) Mass of falling object
Terminal Velocity (Vt): The terminal velocity is returned in meters per second (m/s). However, this can be automatically converted to other velocity units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The formula for terminal velocity is:
Vt= √m⋅gCd⋅ρ⋅A
where:
- Vt = Terminal Velocity
- m = mass of object
- g = acceleration due to gravity
- Cd = drag coefficient
- ρ = density of medium (e.g. air)
- A = Surface area causing drag
Note: Density of air has a default of 1.2754 kg/m3 (IUPAC standard temperature and pressure (0 C and 100 kPa), dry air). The acceleration due to gravity (g) is set to 9.80665 m/s2 for the mean acceleration due to gravity on Earth at Sea Level.
Also note, that if any of the following are zero, the max velocity is infinite since the denominator of the equation is zero. This stands to reason because if:
- ρ is zero, zero density of air would create no resistance.
- C is zero, the shape would be ultimately aerodynamic with no drag.
- A is zero, there would be no exposed surface area and the object would not interact with oncoming atmosphere.
References
- Light and Matter(Dr. Benjamin Crowell) Chapter 4.3 Newton's Second Law
Equations and Data Items
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
