The Bernoulli's Velocity calculator uses Bernoulli's equation to compute velocity (V1) based on the following parameters.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (P1) Pressure at Elevation One
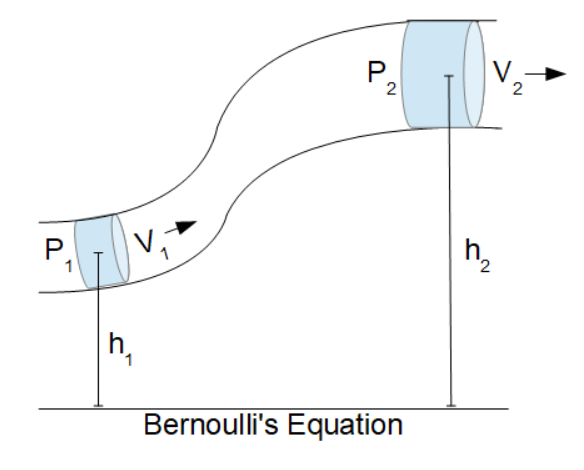
- (h1) Height of Elevation One
- (ρ) Density of the fluid
- (P2) Pressure at Elevation Two
- (V2) Velocity at Elevation Two
- (h2) Height of Elevation Two
Bernoulli's Velocity (V1): The calculator returns the velocity in meters per second. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
Bernoulli Equation Calculators
- Bernoulli's Pressure with any acceleration due to gravity (g)
- Bernoulli's Pressure
- Bernoulli's Velocity
- Bernoulli's Elevation
The Math / Science
Physics | Fluid Mechanics | Bernoulli's Equation] Bernoulli's equation is one of the most important/useful equations in fluid mechanics. Many problems relating to real fluid are analyzed with a form of the Bernoulli equation. Each of the terms in the equation is expressed with units of energy per unit mass. In fluid flow, energy per unit mass is known as head.]
To compute the velocity `V_`1` we start with Bernoulli's equation:
1) `P + 1/2 rho * V^2 + rho *g*h = C` where: C is a constant.
In a combined system with two separate elevations, pressures and velocities (as in the diagram above), the components of the system are associated as:
2) `P_1 + 1/2 rho * V_1^2 + rho *g*h_1 = P_2 + 1/2 rho * V_2^2 + rho *g*h_2`
Based on this, the velocity, `V_1`can be computed using Bernoulli's formula for pressure (`P_1` and `P_2`) and re-ordering the terms of equation 2 :
3) `P_1 = 1/2 rho * (V_2^2 -V_1^2) + rho *g* (h_2-h_1) + P_2`
and then
4) `rho/2 * (V_1^2 -V_1^2) = rho *g* (h_2-h_1) + P_2 -P_1`
5) `V_1^2 -V_2^2= 2/rho*[rho *g* (h_2-h_1) + P_2 -P_1]`
6) `V_1^2 -V_2^2= [2 *g* (h_2-h_1) + 2/rho(P_2 -P_1) ]`
6) `V_1^2 = V_2^2 + [2 *g* (h_2-h_1) + 2/rho(P_2 -P_1) ]`
and then taking the square root:
7) `V_1 = sqrt(V_2^2 +2 *g* (h_2-h_1) + 2/rho(P_2 -P_1) )`
Therefore the formula for Bernoulli's Velocity is:
`V_1 = sqrt(V_2^2 +2 *g* (h_2-h_1) + 2/rho(P_2 -P_1) )`
where:
- V1 is the velocity at elevation 1
- P1 is the pressure at elevation 1 based on Bernoulli's Equation
- h1 is the height of elevation 1
- P2 is the pressure at elevation 2
- V2 is the velocity at elevation 2
- h2 is the height of elevation 2
- ρ is the density of the fluid
- g is the acceleration due to gravity