Processing...
The Continuity Equation states that the product of fluid density (ρ), fluid velocity (V), and cross-section area remains constant in a closed system. In this way, you can use the Continuity Equation to compute one of the parameters for two places in the system if the remain parameters are known.
Mathematically, the Continuity Equation is: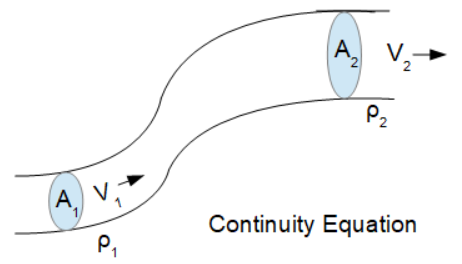
A1 • ρ1 • V1 = A2 • ρ2 • V2
where:
- A1 is the initial cross-section area
- ρ1 is the initial fluid density
- V1 is the initial fluid velocity
- A2 is the final cross-section area
- ρ2 is the final fluid density
- V2 is the final fluid velocity
This calculator has the Continuity Equation solved for:
See Also
Reference
Young, Hugh and Freeman, Roger. University Physics With Modern Physics. Addison-Wesley, 2008. 12th Edition, (ISBN-13: 978-0321500625 ISBN-10: 0321500628 ) Pg 467, eq 14.12