Void Ratio [Total Volume]
Tags | |
UUID | 5f1cd591-d0a5-11e3-b7aa-bc764e2038f2 |
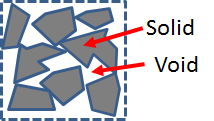
This is an equation for calculating the void ratio of a sample medium. The void represents the relative amount of space occupied by the "voids" in a volume of material, where the voids can be a combination of liquids or gases, and the relative amount of space occupied by the solid material.
This void ratio is a measure of how compact the material is. A volume of large rocks will obviously have a great deal of space between them and thus have a large void ratio compared to fine particulate of a volume of a clay soil, which would have very limited amounts of voids relative to the solid matter.
The inputs to this equation are the total sample volume, VTotal, and the volume observed to be occupied by voids VV.
Notes
In engineering application the void ratio is used to indicate a tendency of a material to expand or contract. A high void ratio is likely to be seen in loose soils which then will contract under pressure or added loads. A low void ratio represents a material that is dense. This void ratio reflects the affect of how fluids will flow through a medium or how particulates can move through the medium.
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
