Distance - initial velocity and constant acceleration
Tags | |
UUID | 78f3b7b3-b95d-11e5-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Distance Calculator uses the equation, ?x= v0??t + ½ a ? ?t2, to calculate the distance traveled (?x) by an object from the origin after a period of time (t), the objects initial velocity (v0) and a constant acceleration (a). 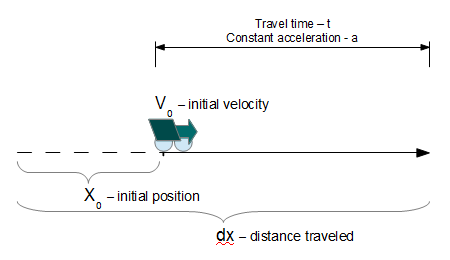 distance traveled
distance traveled
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your preferred units and enter the following:
- (?t) The duration of travel.
- (V0) The initial velocity
- (a) The constant acceleration
Distance: The calculator returns the distance travelled (?x) in meters. However, this can be automatically converted into other length or distance units via the pull-down menu.
Related Calculators:
- Compute the time from the distance and velocity.
- Compute the velocity from the distance and time.
- Compute the distance from the velocity and time.
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity and time
- Distance from initial displacement, velocity, time and constant acceleration
The Math
This equation is a form of the following equation with no initial distance (x0= 0).
dx = x0 + v0•t + ½•a•t2 where x0 is zero.
References
- Light and Matter(Dr. Benjamin Crowell) Chapter 3.6 Algebraic results for constant acceleration
- Light and Matter(Dr. Benjamin Crowell) Chapter 8.4 Calculus with vectors
Notes
A common application for this equation is the travel associated with the free fall of an object under the force of gravity. In the case of Earth's gravity, the constant acceleration is approximately 9.80665 m/s2. Note that this formula does not include other forces such as the force of drag.
See this video discussing a real use for this equation:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=z68vta3N5kg
Equations and Data Items
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
