Tags | |
UUID | 839a5c51-e60d-11e4-a3bb-bc764e2038f2 |
The Acceleration of a Wave calculator computes the acceleration of a wave (y) based on the amplitude (A), angular frequency (ω), location (x), wave number (k) and time (t).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the preferred units and enter the following:
- (A) This is the amplitude
- (ω) This is the angular frequency
- (x) This is the location
- (k) This is the wave number
- (t) This is the time
Wave Acceleration(y): The velocity is returned in meters per second squared (m/s2). However this can be automatically converted into other acceleration units via the pull-down menu.
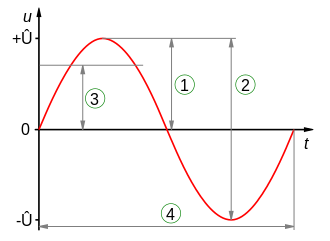 A sinusoidal curve
A sinusoidal curve
- Peak amplitude
- Peak-to-peak amplitude
- Root mean square amplitude
- Wave period
The Math / Science
The Acceleration of a Wave equation is:
where:
- y is the acceleration of the wave
- A is the amplitude
- ω is the angular frequency
- x is the location
- k is the wave number
- t is the time
Reference
Young, Hugh and Freeman, Roger. University Physics With Modern Physics. Addison-Wesley, 2008. 12th Edition, (ISBN-13: 978-0321500625 ISBN-10: 0321500628 ) Pg 496, eq 15.10
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
