Geosynchronous Orbit
| |||||
| |||||
Tags | |
UUID | b33f60aa-5fec-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Geosynchronous Orbit calculator computes the semi-major axis of a geosynchronous orbit based on the peiod.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (P) Orbital Period
Geosynchronous Orbit (a): The semi-major axis is returned in kilometers and nautical miles. However, these can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The Geosynchronous Orbit is an orbit around the Earth with an orbital period of one sidereal day, intentionally matching the Earth's sidereal rotation period (approximately 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds). The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on the surface of the Earth, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky traces out a path, tyically in a figure 8 form, whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit's inclination and eccentricity.
The following formula is used to find the geosynchronous orbit of earth:
a=3 ⎷μ(P(2π)2)
where:
- a = semi-major axis of the orbital ellipse.
- μ = geocentric gravitational constant (398,600.4418 km3/m2)
- P = orbital period
Astronomy Distance Units
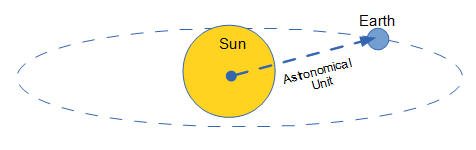
Astronomical Unit (au): Within our solar system, a common measure of distance is au, which stands for astronomical units. A single astronomical unit is the mean distance from the Sun's center to the center of the Earth. The following picture is NOT to scale.
| Astronomical Unit (au) | Distance from Sun (au) |
|---|---|
|
|
Light Travel in Time: Light is a primary observable when studying celestial bodies. For this reason, the distance to these objects are measured in the amount of time it would take light to travel from there to the Earth. We can say that an object is one light-year away, and that means that the object is at a distance where it took an entire year for light from the object to travel to Earth. Since the speed of light is 299,792,458.0 meters per second, one can compute the distance equal to a light year as follows:
1 light year = 299,792,458.0 (meters / second) x 31,536,000 (seconds / year) = 9,460,528,405,000,000 meters
The same exercise can be used for light traveling shorter periods of times, light seconds, light minutes, light hours and light days. Since even these units are not enough when computing distances across the universe, there is also a light relative distance of kilo-light years (1000 light years), or the distance light travels in a thousand years!
| Light Second | Light Minute | Light Hour | Light Day | Light Year | Kilo-Light Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
299,786 km 186,278 miles 0.002 au |
17,987,163 km 11,176,705 miles 0.12023 au |
1,079,229,797 km 670,602,305 miles 7.214 au |
25,901,515,140 km 16,094,455,343 miles 173.14 au |
9,460,528,405,000 km 5,878,499,814,210 miles 63,240 au 0.306 parsecs |
9,460,528,405,000,000 km 5,878,499,814,210,000 miles 63,240,000 au 306 parsecs |
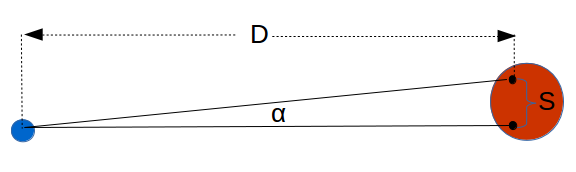
Angle Shift Seen from Earth: Because the Earth goes around the Sun, our observation of distant objects such as stars results in an angular shift when observed at opposite sides of the elliptical orbit. This shift is used as the basis of a unit knows as a parsec. A parsec was traditionally defined as the distance where one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond. A parsec was redefined in 2015 to 648000/π astronomical units. Proxima Centauri, is the nearest star to the Sun and is approximately 1.3 parsecs (4.2 light-years) from the Sun. A mega-parsec is a million parsecs.
| Parsec | Mega-parsec |
|---|---|
|
|
Astronomy Calculators
References
Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geosynchronous_orbit)
Equations and Data Items
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |