Second-order rate law
Tags | |
UUID | bf95b094-207b-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The Second-order Rate calculator computes the second-order chemical reaction rate based on the concentration of substance and a rate constant.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- ([A]) This is the concentration of substance
- (k) This the rate constant
Second-order Rate (R): The calculator returns the rate in moles per liter per second.
Chemistry Rate Law Calculators
- Zero Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Zero Order Half Life
- Zero Order Rate Law
- First Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- First Order Half Life
- First Order Rate Law
- Second Order Rate Law (Integral form)
- Second Order Half Life
- Second Order Rate Law
The Math / Science
The second-order rate law equation[1] calculates the rate at which reactants get converted in to products. The differential form the second-order rate law is dependent on two reactants and thus has two different cases.
Case 1. Both of the reactants (A) are the same
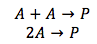 Since both of the reactants are the same, the concentration of A is doubled, this quadruples the rate of the reaction.The rate equation becomes as shown above, where the concentration of substance A is raised to the second power. The rate of reaction is only dependent on the concentration of substance A.
Since both of the reactants are the same, the concentration of A is doubled, this quadruples the rate of the reaction.The rate equation becomes as shown above, where the concentration of substance A is raised to the second power. The rate of reaction is only dependent on the concentration of substance A.
Case 2. Both of the reactants are different
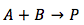
The reactants are different and the equation becomes
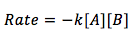
Where both of the reactants are raised to the power of one. The rate of the reaction is dependent on the concentration of substance A and B.
Description
The equation is
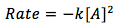 [2]
[2]
where
- [A] is the concentration of some substance A in units of (mol/L)
- k is the rate law constant in units of (L/mol*sec)
Related Topics
Supplement Material
- Khan Academy: Rate law and reaction order
Reference
[1]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rate_equation
[2]Whitten, et al. 10th Edition. Pp. 626,629,631
[Picture]http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Core/Physical_Chemistry/Kinetics/Reaction_Rates/Second-Order_Reactions
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
