The RF Power from voltage and impedance calculator compute the RF Power from the voltage and impedance.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (V) Voltage
- (R) Impedance
RF Power(P): The calculator returns the power in Watts. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The formula for RF Power from voltage and impedance is:
P = V2/R
where:
- P = RF Power
- V = voltage
- R = impedance
RF Power and Voltage Calculators:
- RF Power from dBm
- dBm from RF Power
- Voltage from dBm
- Voltage from RF Power
- dBm from Voltage and Impedance
- RF Power from Voltage and Impedance
Ohm's Law
The Ohm's Law calculator suite computes power (watts), potential (voltage), current (amps) and resistance (ohms) in relation to each other based on Ohm's Law. There is a fundamental relationship between electrical parameters: potential, current, resistance and power depicted in the graphical wheel (see wheel).
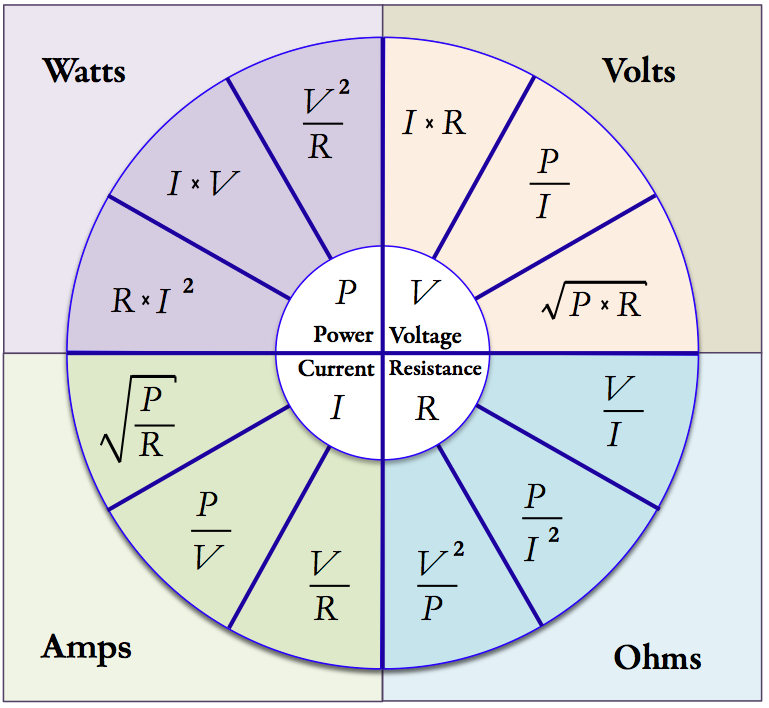
The Ohm's Law Calculator suite has automatic unit conversions for the input and output of the equations. The equations are as follows. Click on the formula for a pop-up calculator with the formula, or click on the description link for the page dedicated to that formula.
Power (watts, milliwatts, kilowatts)
- Power (P) = I • V : Computes the power (watts) as a function of current (amps) and potential (volts).
- Power (P) = R • I² : Computes the power (watts) as a function of current (amps) and resistance (ohms).
- Power (P) = V² / R: Computes the power (watts) as a function of potential (volts) and resistance (ohms).
Potential (volts, millivolts)
- Volts (V) = I • R : Computes the potential (volts) as a function of current (amps) and resistance (ohms).
- Volts (V) = P / I : Computes the potential (volts) as a function of power (watts) and current (amps).
- Volts(V) = √(P • R) : Computes the potential (volts) as a function of power (watts) and resistance (ohms).
Resistance (ohms, milliohms, kiloohms)
- Resistance (R) = V²/P : Computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of potential (volts) and power (watts).
- Resistance (R) = P / I² : Computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of power (watts) and current (amps).
- Resistance (R) = V / I : Computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of potential (volts) and current (amps).
Current (amps, milliamps, microamps, gilberts)
- Current (I) = V / R : Computes the current (amps) as a function of potential (volts) and resistance (ohms).
- Current (I) = P / V : Computes the current (amps) as a function of the power (watts) and the potential (volts).
- Current (I) = √(P/R) : Computes the current (amps) as a function of the power (watts) and the resistance (ohms).

