The Surface Area of an Oblate Spheroid calculator 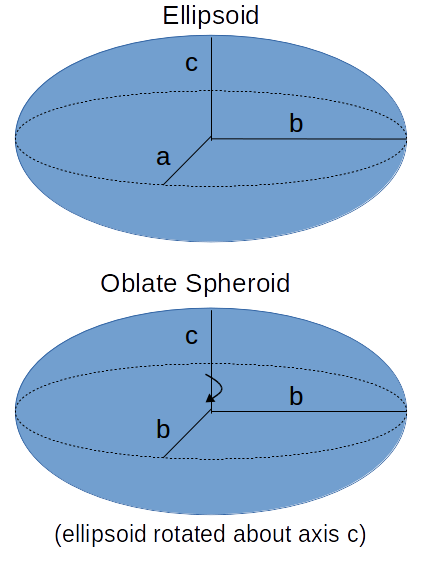 approximates the surface area of an oblate spheroid.
approximates the surface area of an oblate spheroid.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:.
- (b) Semi-major Axis (Distance from the oblate spheroid's center along the longest axis of the spheroid)
- (c) Semi-minor Axis (D istance from the oblate spheroid's center along the shortest axis of the spheroid)
Surface Area of Oblate Spheroid (sA): The area is returned in square meters. However, this can be an automatically converted to many other area units (e.g. square inches or acres) via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The oblate spheroid is an ellipsoid that can be formed by rotating an ellipse about its minor axis. The rotational axis thus formed will appear to be the oblate spheroid's polar axis. The oblate spheroid is fully described then by its semi-major and semi-minor axes.
The formula for the surface area of an Oblate Spheroid is as follows:
sA = 2πb2(1 + (1-e2)/e * tanh-1e) where e2 = 1 - c2/b2
One important shape in nature that is close to (though not exactly) an oblate spheroid is the Earth.
Ellipsoid Calculator
Ellipsoid - Volume computes the volume of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Surface Area computes the surface area of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c)
- Ellipsoid - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an ellipsoid based on the length of the three semi-axes (a, b, c) and the mean density.
- Ellipsoid Cap - Volume computes the volume of a section of an ellipsoid.
- Oblate Spheroid - Volume computes the volume of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Surface Area computes the surface area of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c)
- Oblate Spheroid- Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of an Oblate Spheroid based on the length of the two semi-axes (b, c) and the mean density.
- Sphere - Volume computes the volume of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Surface Area computes the surface area of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a)
- Sphere - Mass or Weight computes the mass or weight of a sphere based on the length of the radius (a) and the mean density.
- Circular - Volume: Computes the volume of a column with a circular top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Circular - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of circular volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Elliptical Volume: Computes the volume of a column with an elliptical top and bottom and vertical sides.
- Elliptical - Mass: Computes the mass/weight of an elliptical volume based on its dimensions and mean density.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Edge (VE): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Vertical Chord from Center (VC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Edge (HE): Computes the length of the horizontal chord of an ellipse based on distance from the edge.
- Ellipse Horizontal Chord from Center (HC): Computes the length of the vertical chord of an ellipse based on distance from the center.
- Common Mean Density: Provides a lookup function to find the mean density of hundreds of materials (woods, metals, liquids, chemicals, food items, soils, and more)