Tags | |
The Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids calculator compute the velocity based on the inner radius and length of a pipe, the viscosity of the fluid and the input and output pressure.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
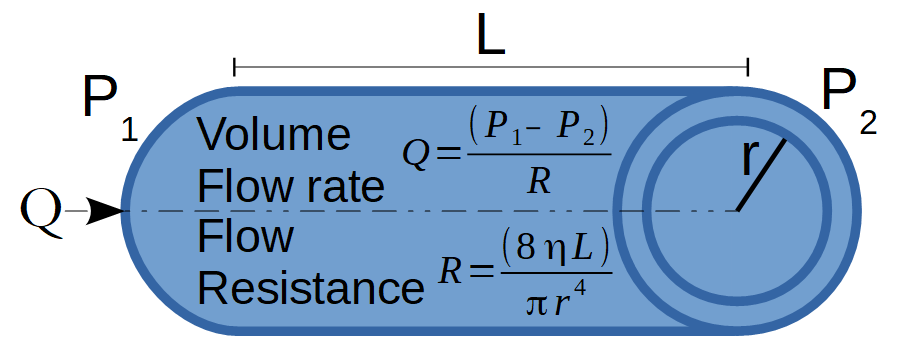
- (r) This is the inner radius of the tube
- (P1) This is the input pressure
- (P2) This is the output pressure
- (μ) This is the viscosity of the fluid
- (L) is the length of tube
Fluid Velocity (v): The calculator returns the velocity in cm/s. However this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down men.
Related Calculators
- Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance
- Poiseuille's Law
- Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids
- Compute the Heart Chamber Pressure via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Heart Wall Stress via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Blood Flow Rate using Darcy's Law
- Compute the Change in Vascular Pressure
- Compute Blood Pressure
The Math / Science
In nonideal fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation, also known as the Hagen–Poiseuille law, Poiseuille law or Poiseuille equation, is a physical lawthat gives the pressure drop in an incompressible and Newtonian fluid in laminar flow flowing through a long cylindrical pipe of constant cross section. It can be successfully applied to air flow in lung alveoli, for the flow through a drinking straw or through a hypodermic needle. It was experimentally derived independently byGotthilf Heinrich Ludwig Hagen in 1839 and Jean Léonard Marie Poiseuille in 1838, and published by Poiseuille in 1840 and 1846.
The assumptions of the equation are that the fluid is incompressible and Newtonian; the flow is laminar through a pipe of constant circular cross-section that is substantially longer than its diameter; and there is no acceleration of fluid in the pipe. For velocities and pipe diameters above a threshold, actual fluid flow is not laminar but turbulent, leading to larger pressure drops than calculated by the Hagen–Poiseuille equation.
The velocity equation for Poiseuile's Law is:
v=r216·μ
where:
- v is the velocity of compressible fluid
- r is the inner radius of the tube
- P1 is the input pressure
- P2 is the output pressure
- μ is the viscosity
- L is the length of tube
References
The definition and formula for Poiseuille's equation for the compressible fluids was taken from Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hagen%E2%80%93Poiseuille_equation).

