Tags | |
The Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance calculator computes the fluid resistance in a blood vessel or small tube based on the viscosity (η) and length (L) and radius (r) of the vessel.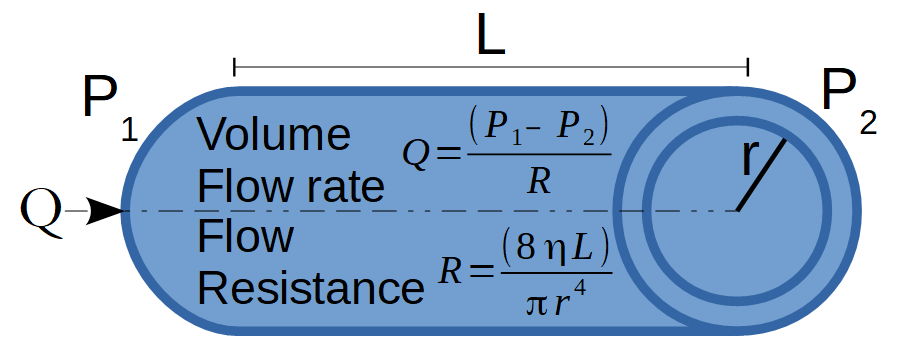
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose your preferred units and enter the following:
- (η) Fluid Viscosity.
- (L) Length of Vessel.
- (r) Inner Radius of Vessel.
Tube/Vessel Resistance (R): The calculator returns the resistance (R) in mmHg•min / L.
The Math / Science
Poiseuille's Law relates the fluid resistance of blood flow through a small blood vessel with the blood vessel's radius (r), the length (λ) of the artery, and the viscosity (η) of the blood. The formula for Poiseuille's Law of Blood Resistance is:
R=8•η•λπ•r4
where:
- R is the Blood Flow Resistance
- η is the viscosity
- λ is the length of the blood vessel or artery
- r is the interior radius of the blood vessel or artery
The volume of a homogeneous fluid passing per unit time through a capillary tube without turbulence is proportional to the pressure difference between its ends and is proportional to the fourth power of its internal radius.
The volumetric flow rate is also inversely proportional to the length of the tube and the viscosity of the fluid. This formula applies to the flow of blood in an artery because we can treat the blood flow as a laminar flow of a uniformly viscous liquid.
Cardiac and Blood Flow Calculators
- Hagen-Poiseuille Resistance
- Poiseuille's Law
- Poiseuille's Velocity of Compressible Fluids
- Compute the Heart Chamber Pressure via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Heart Wall Stress via the Law of Laplace
- Compute the Blood Flow Rate using Darcy's Law
- Compute the Change in Vascular Pressure
- Compute Blood Pressure
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP): Calculates MAP from Pulse Pressure and Diastolic Pressure
- Mean Arterial Pressure and Pulse Pressure: Calculates MAP and Pulse Pressure from Diastolic Pressure and Systolic Blood Pressure
- Cardiac Output from Heart Rate and Stroke Volume

