Processing...
`P = I * V`
Enter a value for all fields
The Electrical Power calculator computes the power based on Ohm's Law using electrical potential or voltage (V) and current (I).
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (V) Potential (voltage)
- (I) Current.
Electrical Power: The calculator returns the electrical power in watts. However, this can be automatically converted to other power units via the pull-down menu.
General Information
For more information on the relationship between electrical power, current, resistance and potential, see the Ohm's Law Calculator.
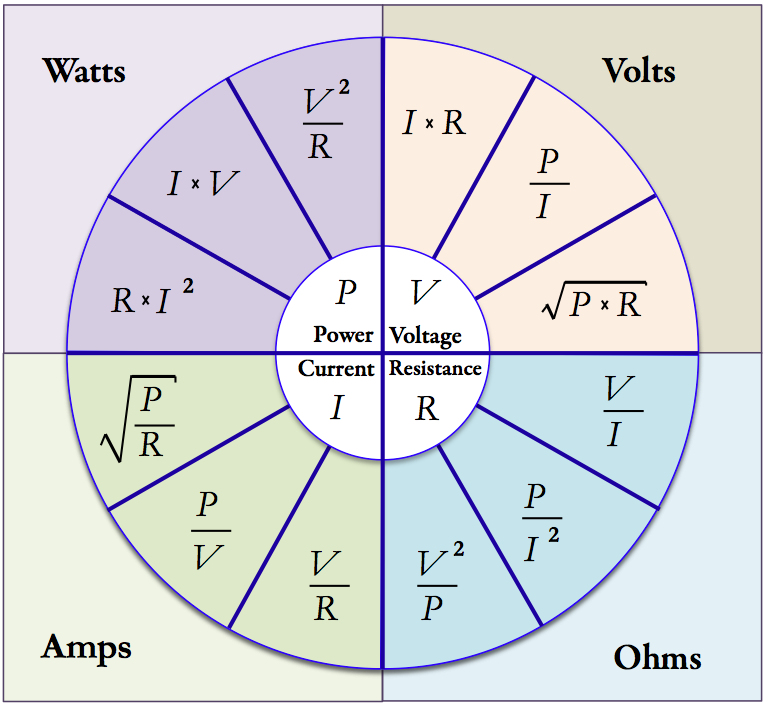
- Power: (watts, milliwatts, kilowatts, horsepower)
- Potential: (volts, millivolts)
- V = I • R : This computes the potential (volts) as a function of current (amps) and resistance (ohms).
- V = P / I: This computes the potential (volts) as a function of power (watts) and current (amps).
- V = √(P • R) : This computes the potential (volts) as a function of power (watts) and resistance (ohms).
- Resistance: (ohms, milliohms, kiloohms)
- R = V²/P: This computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of potential (volts) and power (watts).
- R = P / I² : This computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of power (watts) and current (amps).
- R = V / I : This computes the resistance (ohms) as a function of potential (volts) and current (amps).
- Current: (amps, milliamps, microamps, gilberts)
- I = V / R: This computes the current (amps) as a function of potential (volts) and resistance (ohms).
- I = P / V : This computes the current (amps) as a function of the power (watts) and the potential (volts).
- I = √(P/R): This computes the current (amps) as a function of the power (watts) and the resistance (ohms).
Power is the amount of energy consumed or produced over time.
- Power is a measurement of the energy used to move vehicles (automobiles, trucks, tractors, trains, boats and airplanes).
- Power is the measurement of energy consumed by a motor and transferred to the drive or wheels.
- Power is the amount of electrical energy consumed or produced by a system over time such as the energy produced by a hydroelectric dam or energy consumed by an electrical motor.
Power Units
Power is most commonly measured in watts (W). One watt is equal to one joule per second (1 W = 1 J / 1 s). Power is also measured in horsepower (hp) where 1 horsepower equals 745.7 watts. Power is also measured in heat energy transfer as BTUs per hour (BTU/h).
Power Calculators
- Power from Change in Energy over Time
- Power based on Force and Velocity
- P = ΔE / Δt
- ΔE = P * Δt
- Δt = ΔE / P
- Power Dissipated by Friction
- Power from Force, Distance and Time
- Power from Resistance and Current
- Power from Voltage and Resistance
- Power from Current and Voltage
- Power textbook chapter (Light and Matter)