The Charles Law Calculator computes the initial and final volumes and temperatures using Charles Law: (V1•T2 = V2•T1 ). The calculator automatically hands numerous temperature and volume units . The formula used in these computations are all derived from the simple Charles Law relationship (click on a parameter):
V1 • T2 = V2 • T1
- (V1) Initial Volume
- (V2) Resulting or Final Volume
- (T1) Initial Temperature
- (T2) Resulting or End Temperature
See YouTube video instructions HERE.
Charles Law is represented mathematically as: V/T = k as the animated image below represents.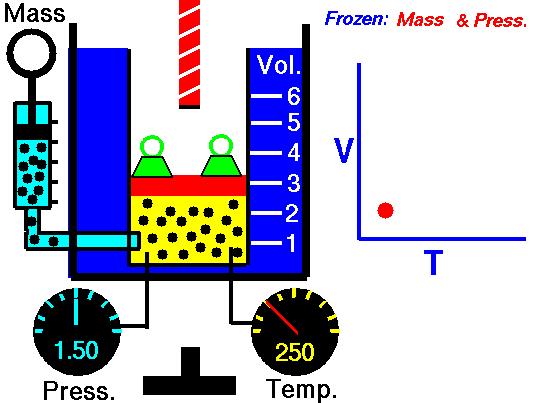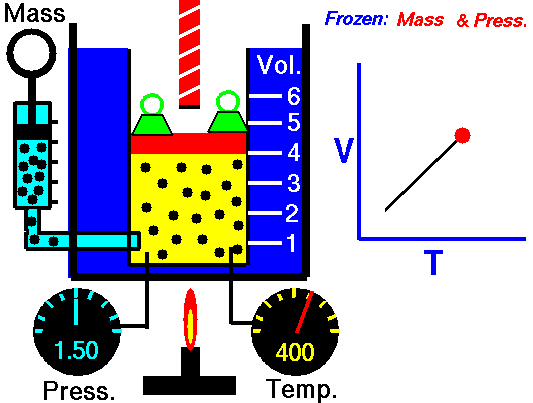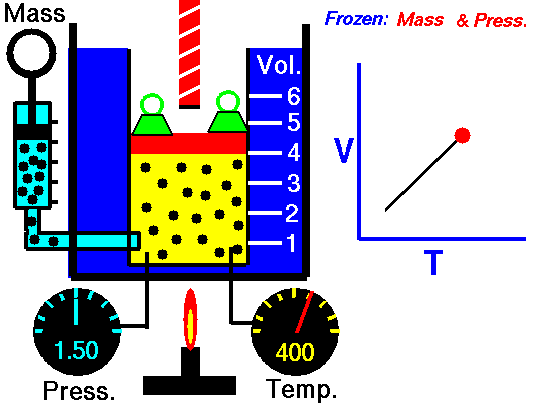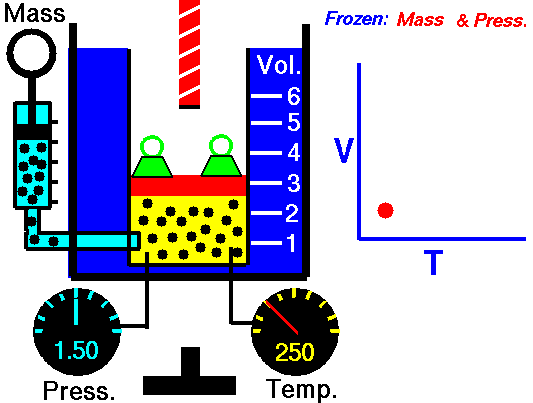 Image courtesy of Wikipedia
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
APPLICATIONS
There are many applications for this equation where you can measure the temperature and volume conditions before and after changes to either volume of temperature of a fixed amount of gas.
Here are some examples:
- If you construct a mechanical apparatus like the one show in the picture at the right, where the gas is allowed to increase in volume while you maintain the pressure constant (shown by the pressure gauge and the small green weights exerting a constant force on the top of the container), then the heat applied will cause the volume of the gas to increase. Try this our using the equation Charles Law (Final Volume).
- Volume will increase (causing motion in a flexible container like the one shown in the image) anytime the temperature is increased.
- Temperature will decrease anytime you cause the volume to decrease. Try this our using the equation Charles Law (Final Temperature).
EQUATIONS
Charles Law (Final Temperature) - Charles Law computing the temperature of a fixed mass of gas which results when the volume changes
Charles Law (Initial Temperature) - Charles Law computing the starting temperature of a fixed mass of gas before a change in volume occurred
Charles Law (Final Volume) - Charles Law computing the volume of a fixed mass of gas after it undergoes a temperature change
Charles Law (Initial Volume) - Charles Law computing the starting volume of a fixed mass of gas before it underwent a temperature change
NOTES
Charles' law is also known as the law of volumes. It is an experimental gas law which describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles's law is:
When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be directly related. [1]
Chemistry Calculators
- R - Gas Constant: 8.3144626181532 J/(K⋅mol)
- Boyle's Law Calculator: P1 • V1 = P2 • V2
- Charles Law Calculator: V1• T2 = V2 • T1
- Combined Gas Law Calculator: P•V / T= k
- Gay-Lussac Law: T1•P2 =T2•P1
- Ideal Gas Law: P•V = n•R•T
- Bragg's Law: n·λ = 2d·sinθ
- Hess' Law: ΔH0rxn=ΔH0a+ΔH0b+ΔH0c+ΔH0d
- Internal Energy: ΔU = q + ω
- Activation Energy: Ea = (R*T1⋅T2)/(T1 - T2) ⋅ ln(k1/k2)
- Arrhenius Equation: k = AeE_a/(RT)
- Clausius-Clapeyron Equation: ln(P2/P1) = (ΔHvap)/R * (1/T1 - 1/T2)
- Compressibility Factor: Z = (p*Vm)/(R*T)
- Peng-Robinson Equation of State: p = (R*T)/(Vm - b) - (a*α)/(Vm2 + 2*b*Vm - b2)
- Reduced Specific Volume: vr = v/(R* Tcr / Pc)
- Van't Hoff Equation: ΔH0 = R * ( -ln(K2/K1))/ (1/T1 - 1/T2)
