Tags | |
UUID | e534af65-2c60-11e6-9770-bc764e2038f2 |
The buoyancy equation in chemistry, is used to correct the mass obtained from a measurement made on a balance, specifically when the mass obtained from the balance does not correspond to the object's standard mass density. In physics buoyancy is defined as the upward force on an object which is found in air, gas or liquid.
Description
The equation is
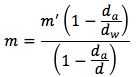
where
- m' is the mass read on balance in units of (g)
- da is the density of air which is 0.0012g/mL near 1 bar and 25oC
- dw is the density of calibration weights which is 8.0g/mL
- d is the density of object being weighed in units of (g/mL)
- m is the mass of the object weighed in a vacuum in units of (g)
References
Harris, D., Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 9th Ed., W. H. Freeman, Pp.29 (2015).
This equation, Buoyancy Equation, is used in 1 page
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
