Processing...
`|vecv| = sqrt( v_x ^2 + v_y ^2 + v_z ^2)`
Enter a value for all fields
The Magnitude of a Velocity Vector calculator computes the magnitude of velocity based on the three orthogonal components.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (vx) X component of velocity
- (vy) Y component of velocity
- (vz) Z component of velocity
Velocity Vector Magnitude (`|vecv|`): The calculator returns the magnitude in meters per second. However, this can be automatically converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
Magnitude Calculators
- Magnitude of Position Vector
- Magnitude of Velocity Vector
- Magnitude of Acceleration Vector
- Magnitude of Force Vector
- |V| Magnitude of a vector
3D Vector Functions
 k⋅V - scalar multiplication
k⋅V - scalar multiplication- V/k - scalar division
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- V x U • W - Computes the mixed product of three vectors
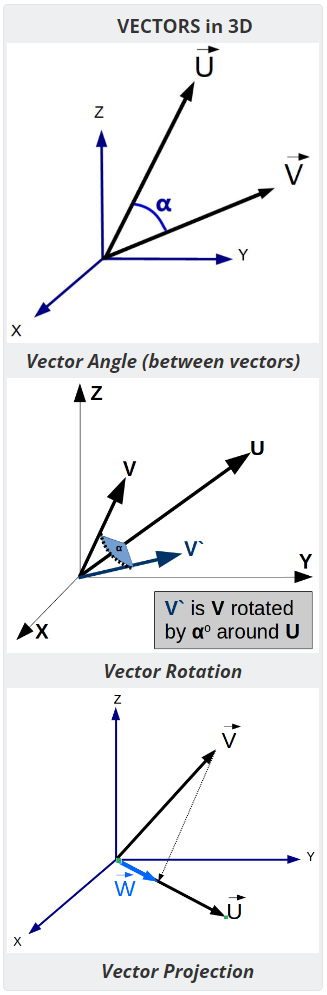
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Area - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- Vector Components 3D - Returns a vector's magnitude, unit vector, spherical coordinates, cylindrical coordinates and angle from each axis.
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
- (x,y) to (r, θ) - Cartesian to Polar
- (r, θ) to (x,y) - Polar to Cartesian
- Vector Normal to a Plane Defined by Three Points
Reference
University Physics 12th Edition, Chapter 3, Equation #3.6
