The Deck Boards Count calculator computes the number of decking boards required for a floor or deck based on the dimension of the room or deck and the specifications of the boards.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (L) Length of Deck or Floor (running with joists)
- (W) Width of Deck or Floor (spanning across joists)
- (BL) Decking Board Length
- (BW) Decking Board Width
- (JS) Joist Spacing
Number of Boards (nB): The calculator returns the number of decking boards needed to achieve the specified surface area. If the width (W) is less than 24 feet, the calculator also returns an alternative count using board lengths (BL) requiring no splicing.
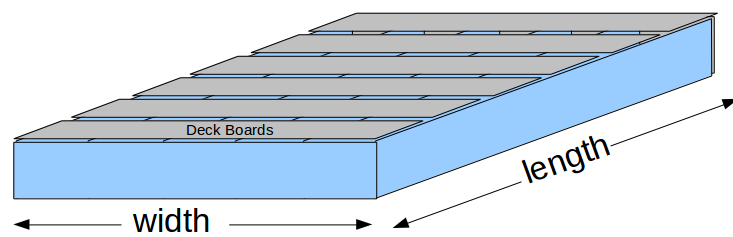 Decking Boards
Decking Boards 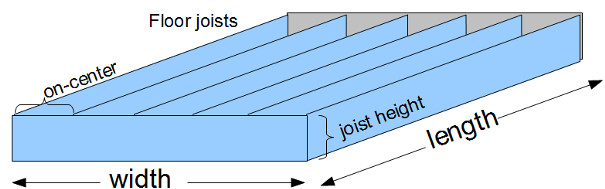 Floor Joists and Plates (end pieces).
Floor Joists and Plates (end pieces).
The Math / Science
The most common decking board are pressure treated pine boards that are six inches (6") wide and at different length ranging from three feet (3') to twenty four feet (24') in North America. The North American boards are actually 5.5 inches wide. The assumption is a half inch gap between the boards.
Deck boards are either laid perpendicular to (across) the floor or deck joists, or on a diagonal pattern. The goal is to transfer the weight on the deck boards to the floor joist in a short distance. Never run the deck boards parallel to the floor joists.
You should NEVER splice decking boards between joists. Splices should always occur where both board ends are on top of a joist, and in many cases, boards must be shortened (cut off) to end at a joist. The algorithm used in this calculator uses the joist span to estimate the cut-off of the decking boards.
Choosing the Right Length Deck Boards
When the width of your deck is longer than the length of your boards, splicing is required. If possible, you might want to consider longer boards if they are available. Longer boards will reduce or eliminate splicing which saves labor, and in some cases may even save material costs. For example, at the time of this writing, a nationally advertised provider of decking boards listed 5/4" thick, pressure treated, six inch wide deck boards that were $6.84 for 8' boards and $8.70 for 10' boards. In the graphic below, you can see where 10' boards only required 12 boards to cover the deck and 8' boards required 17 boards and 13 splices. In this case, the 10' boards ended up costing less at $104.40 verses $116.28.
Deck Board Materials
Decking boards, the planks that make up the surface of a deck, can be constructed from a variety of materials. Each material has its own set of characteristics, including durability, appearance, maintenance requirements, and cost. Here are some common materials used for decking boards:
- Wood Decking (Natural):
- Pressure-Treated Pine: This is one of the most common and affordable options. It's treated with preservatives to resist decay, insects, and moisture. However, it requires periodic maintenance to maintain its appearance.
- Cedar: Known for its natural beauty and resistance to decay, cedar is a popular choice. It has a distinctive reddish-brown color and a pleasant aroma. It's more expensive than pressure-treated pine.
- Redwood: Similar to cedar, redwood is naturally resistant to decay and insects. It's known for its rich, reddish-brown color and durability. It's one of the more expensive wood options.
- Exotic Hardwoods (e.g., Ipe, Tigerwood): These tropical hardwoods are incredibly dense, durable, and resistant to decay. They have unique, rich colors and are known for their longevity. They are among the most expensive options.
- Composite:
- Composite Decking: Made from a combination of wood fibers and plastic, composite decking offers durability, low maintenance, and resistance to rot, insects, and UV rays. It comes in a wide range of colors and styles, simulating the look of wood.
- Plastic:
- PVC Decking: Made entirely of polyvinyl chloride, PVC decking is highly durable and resistant to moisture, mold, and insects. It doesn't require sealing or staining, but it can be more expensive than other options.
- Aluminum:
- Aluminum Decking: Known for its strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and insects, aluminum decking is often used in coastal areas or near water. It's low maintenance but can be more expensive upfront.
- Bamboo:
- Bamboo Decking: This is an eco-friendly option made from bamboo fibers and recycled plastics. It's durable and has a unique appearance, but availability may vary depending on location.
Deck Builder Calculator provides estimates for a simple rectangular deck project. Calculator functions include the following:
- Deck Board Count: Computes the number of decking boards needed for your deck based on the size of the deck and the size of the decking boards.
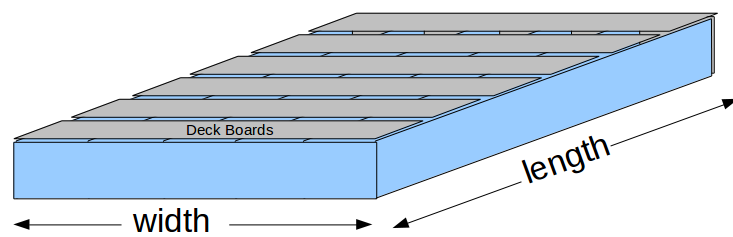
- Deck Boards Cost: Computes the cost of deck board flooring based on a computed number of deck boards and the price per board.
- Decking Cost Estimate: Estimates the cost of wood board decking based on total area and unit pricing in dollars per square feet.
- Subfloor 4x8 Sheets: Computes the number of 4x8 sheets to cover floor/deck area.
- Subfloor Cost: Computes the cost of 4x8 sheets to cover fool/deck area.
- Deck Joist Count: Computes the number of floor joists needed for a deck. It returns the number of joists and plate boards, square feet of area and the length of the diagonal.
- Joists on Beams
: Computes the number of joists (2x dimensional lumber or i-joists), number of beams, number of joist hangers, and length of plate boards needed for a floor or deck with a span that might require one or more beams.
- Deck Joist Cost: Computes the total cost of the floor joist boards.
- Deck Stain and Sealer: Computes the amount of stain and sealer needed for a deck.
