LM 29.3 A real image Collection
Tags | |
UUID | 1ee1b498-f145-11e9-8682-bc764e2038f2 |
29.3 A real image by Benjamin Crowell, Light and Matter licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license.
29.3 A real image
If we start by placing an object very close to the mirror, g/1, and then move it farther and farther away, the image at first behaves as we would expect from our everyday experience with flat mirrors, receding deeper and deeper behind the mirror. At a certain point, however, a dramatic change occurs. When the object is more than a certain distance from the mirror, g/2, the image appears upside-down and in front of the mirror.
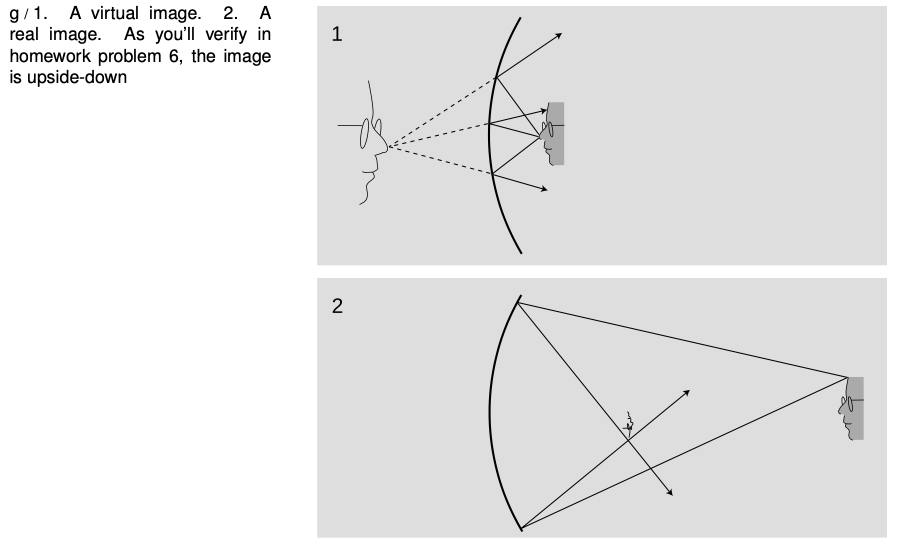
Here's what's happened. The mirror bends light rays inward, but when the object is very close to it, as in g/1, the rays coming from a given point on the object are too strongly diverging (spreading) for the mirror to bring them back together. On reflection, the rays are still diverging, just not as strongly diverging. But when the object is sufficiently far away, g/2, the mirror is only intercepting the rays that came out in a narrow cone, and it is able to bend these enough so that they will reconverge.
Note that the rays shown in the figure, which both originated at the same point on the object, reunite when they cross. The point where they cross is the image of the point on the original object. This type of image is called a real image, in contradistinction to the virtual images we've studied before.

The use of the word “real” is perhaps unfortunate. It sounds as though we are saying the image was an actual material object, which of course it is not.
The distinction between a real image and a virtual image is an important one, because a real image can be projected onto a screen or photographic film. If a piece of paper is inserted in figure g/2 at the location of the image, the image will be visible on the paper (provided the object is bright and the room is dark). Your eye uses a lens to make a real image on the retina.
self-check:
Sketch another copy of the face in figure g/1, even farther from the mirror, and draw a ray diagram. What has happened to the location of the image?
(answer in the back of the PDF version of the book)
29.3 A real image by Benjamin Crowell, Light and Matter licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license.
Calculators and Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
