Polar to Cartesian
`(x,y) = f(r,theta)`
Tags | |
UUID | 2848bd41-660b-11ef-98f1-bc764e203090 |
The Polar to Cartesian Coordinates calculator computes the 2D coordinates for a vector given based on the polar coordinates.
INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following:
- (r) Radius
- (θ) Polar Angle
Cartesian Coordinates (x,y): The calculator returns the vector as a real numbers.
The Math / Science
The formula for Cartesian to Polar coordinates is:
- x = r ⋅ cos(θ)
- y = r ⋅ sin(θ)
where:
- r = magnitude of the (x,y) vector
- θ = polar angle
- (x,y) = coordinates of (x,y) vector
Polar coordinates are a two-dimensional coordinate system in which a point in the plane is determined by its distance from a reference point and the angle relative to a reference direction.
Here’s how polar coordinates work:
- Reference Point (Pole): The fixed point in the system is called the pole, typically represented as the origin (0, 0) in Cartesian coordinates.
- Radial Distance (r): The distance from the pole to the point in question. It is always a non-negative value (r ≥ 0).
- Angle (θ): The angle measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis to the line connecting the point to the pole. The angle can be in degrees or radians and can be positive (counterclockwise direction) or negative (clockwise direction).
In polar coordinates, a point is represented as (r,θ), where:
- r is the radial distance.
- θ is the angle.
Polar Coordinate Calculators
- (x,y) to (r, θ) - Cartesian to Polar
- (r, θ) to (x,y) - Polar to Cartesian
3D Vector Functions
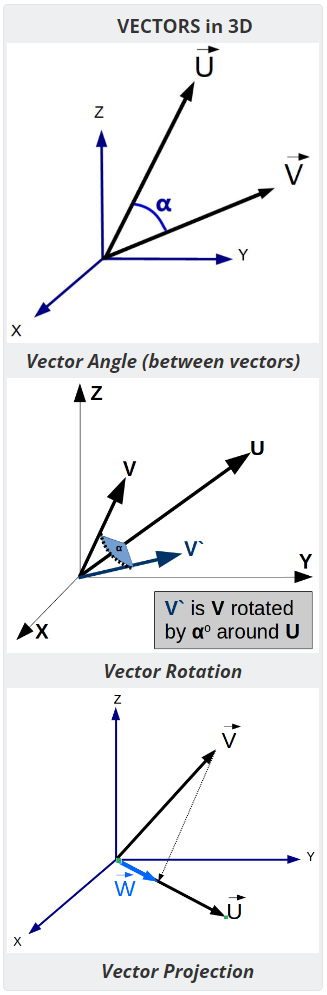 k⋅V - scalar multiplication
k⋅V - scalar multiplication- V/k - scalar division
- V / |V| - Computes the Unit Vector
- |V| - Computes the magnitude of a vector
- U + V - Vector addition
- U - V - Vector subtraction
- |U - V| - Distance between vector endpoints.
- |U + V| - Magnitude of vector sum.
- V • U - Computes the dot product of two vectors
- V x U - Computes the cross product of two vectors
- V x U • W - Computes the mixed product of three vectors
- Vector Angle - Computes the angle between two vectors
- Vector Area - Computes the area between two vectors
- Vector Projection - Compute the vector projection of V onto U.
- Vector Rotation - Compute the result vector after rotating around an axis.
- Vector Components 3D - Returns a vector's magnitude, unit vector, spherical coordinates, cylindrical coordinates and angle from each axis.
- (ρ, θ, φ) to (x,y,z) - Spherical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (ρ, θ, φ) - Cartesian to Spherical coordinates
- (r, θ, z) to (x,y,z) - Cylindrical to Cartesian coordinates
- (x,y,z) to (r, θ, z) - Cartesian to Cylindrical coordinates
- (x,y) to (r, θ) - Cartesian to Polar
- (r, θ) to (x,y) - Polar to Cartesian
- Vector Normal to a Plane Defined by Three Points
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
This site uses cookies to give you the best, most relevant experience. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.

