Alveolar gas equation
Tags | |
UUID | e6d2a3d4-da27-11e2-8e97-bc764e04d25f |
The Alveolar Gas calculator computes the partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary alveoli based on the fraction of oxygen in the inhaled gas, the atmospheric pressure, the ratio of CO2 to O2 , the saturated vapor pressure, and the partial pressure of the CO2.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose the preferred units and enter the following:
- (FiO2) - This is the fraction of the inhaled gas this is oxygen after it has been humidified at body temperature.
- (P(ATM)) - This is the pressure (force per unit area) exerted at the surface of the Earth by the Earth's atmosphere.
- (RQ) - This is the ratio of CO2 produced to O2 consumed while breathing
- (pH2O) - This is the saturated vapor pressure, the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium, of water at body temperature & atmospheric pressure
- (paCO2) - This is the partial pressure that a gas (CO2), included in a gas mixture (air breathed), would exert if it were contained in the same volume as the mixture (air breathed) and at the same temperature
Alveolar Partial Pressure: The alveolar partial pressure is given in kPa. However, this can be automatically converted to other pressure units via the pull-down menu.
The Math / Science
The pulmonary alveolar partial pressure is used to calculate the alveolar-arterial gradient of oxygen and the amount of right-to-left cardiac shunt. The Alveolar Gas Equation is as follows:
- (pA02= FIO2 * (PATM - pH2O ) - (paCO2 * (1 - FIO2 * (1 - RQ))) / (RQ) )
REFERENCE
Any reference that follows the Creative Common Attribution ShareAlike License model …
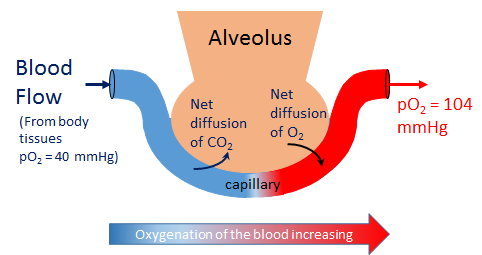
[1] Alveolar Gas Equation
Creator: Wikipedia
URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pulmonary_alveolus
Public License: CC Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International
[1] Pulmonary alveolus
Creator: Wikipedia
URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolar_gas_equation
Public License: CC Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International
[2] Alveolar-arterial gradient
Creator: Wikipedia
URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alveolar%E2%80%93arterial_gradient
Public License: CC Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International
NOTES
The equation relies on the following assumptions:
- Inspired gas contains no carbon dioxide (CO2) or water
- Nitrogen (and any other gases except oxygen) in the inspired gas are in equilibrium with their dissolved states in the blood
- Inspired and alveolar gases obey the Ideal Gas Law
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) in the alveolar gas is in equilibrium with the arterial blood i.e. that the alveolar and arterial partial pressures are equal
- The alveolar gas is saturated with water
vCalc content is available under the Creative Common Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. vCalc also provides terms of use and a privacy policy.
Calculators
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |
