The Lifting Torque for a Leadscrew calculator computes the torque required to lift a load with a square thread power screw assembly.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following: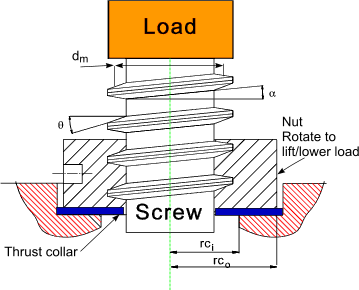 Leadscrew Square Thread
Leadscrew Square Thread
- (L) Lead (linear distance the nut moves per full revolution)
- (F) Load
- (dm) Mean Thread Diameter
- (μ) Coefficient of Friction for Thread (Default: 0.2)
Lifting Torque (TR): The calculator returns the torque in Newton meters (N m). However, this can be converted to compatible units via the pull-down menu.
| Screw Metal | Nut Metal | |||
| Steel | Bronze | Brass | Cast Iron | |
| Dry Steel | 0.15-0.25 | 0.15-0.23 | 0.15-0.19 | 0.15-0.25 |
| Machine Oiled Steel | 0.11-0.17 | 0.10-0.16 | 0.10-0.15 | 0.11-0.17 |
| Bronze | 0.08-0.12 | 0.04-0.06 | N/A | 0.06-0.09 |
Related Calculators
The Math / Science
The Leadscrew Lifting Torque equation is:
`T_R= F*d_m/2((L+pi*μ*d_m)/ (pi*d_m- μ*L)) `
where:
- TR is the torque required to raise a load using a Square Thread Power Screw assembly.
- dm is the mean thread diameter
- dc is the mean collar diameter
- L is the lead
- F is the load
- μ is the coefficient of friction for thread
Leadscrews
A leadscrew is a mechanical device that converts rotational motion into linear motion. It consists of a threaded shaft and a mating nut that moves along the shaft when it is rotated. Leadscrews are commonly used in applications requiring precise linear movement, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, lathes, and linear actuators.
Key Features of a Leadscrew:
- Threaded Shaft: The screw has helical threads that engage with the nut.
- Nut: The component that moves along the shaft when it rotates.
- Linear Motion: Rotating the screw causes the nut to move in a straight line.
- High Precision: Often used in precision positioning applications.
Types of Leadscrews:
- Acme Leadscrew: Has a trapezoidal thread shape for strength and durability.
- Square Leadscrew: Provides high efficiency but is harder to manufacture.
- Ball Screw: Uses ball bearings to reduce friction, improving efficiency and longevity.
- Buttress Thread Leadscrew: Designed for heavy loads in one direction.
Advantages:
✔ Simple design
✔ Self-locking (in most cases, prevents backdriving)
✔ Precise control over motion
Disadvantages:
❌ Lower efficiency due to friction
❌ Limited speed compared to ball screws
Simple Machine Calculators
- Lever Beam Length: Computes the length of a lever (beam) on one side of a fulcrum needed to lift an object based on the objects weight and the length of the beam on the other side of the fulcrum.
- Leverage Lift Weight: Computes the weight that can be lifted using a lever based on the downward force and the length of the lever on either side of the fulcrum.
- Fulcrum Position (x): Computes the position of the fulcrum needed in a lever to lift a weight (W) with a downward force (F) with a beam of length (L), where L = x + y.
- Belt Length: Computes the length of a belt that goes around two pulleys of different diameters separated by a specific distance.
- Belt Speed: Computes the speed a belt travels based on the diameter of the pulley and the RPMs.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a pulley based on the speed of the belt and the diameter of the pulley.
- 2nd Pulley RPMs: Computes the RPMs of a second pulley in a two pulley system when the RPM and Diameter are known for one pulley and the diameter of the second pulley is also known.
- 2nd Pulley Diameter:- Computes the diameter of a second pulley in a two pulley system based on diameter and RPM of one pulley and the RPMs of the second.
- Pulley System Tension: Computes the tension on a cable around a cable based on two weights.
- Pulley System Acceleration: Computes the belt or cable acceleration in a two mass pulley system.
- RPM of 4th pulley on three shafts: Computes the RPMs of a fourth pulley on
a three shaft system when the RMPs of the first shaft is known and the four diameters.
- 2nd Gear RPM: Computes the RPMs of a second gear when the RPM and number of teeth are known for the first gear, and the number of teeth are known for the second gear.
- Pulley RPMs: Computes pulley RPMs from belt speed and pulley diameter.
- Sum of Two Lengths: Computes the sum of two lengths (useful with lever calculations).
- Second Gear Torque: Calculates the torque of a second gear when the torque and number of teeth are known for the first gear and the number of teeth of the second gear is known.
- Leadscrew Torque (lift): Computes the torque required to lift a load with a square thread power screw assembly.
