Concrete Displaced by Rebar
The Concrete Displaced by Rebar calculator estimates the net weight added to a slab by adding rebar, and the reduction in concrete cause by adding rebar.
INSTRUCTIONS: Choose units and enter the following:
- (L) Length of Rebar
- (rS) Size of Rebar (2-11,14,18)
Weight and Volume Change from Rebar added to Slab (W and V): The calculator returns the following weights and volumes in standard units. However, these units can be automatically converted compatible units (e.g., cubic yards to cubic meters) via the pull-down menu.
- (-CV) Volume of concrete displaced by rebar in cubic yards (yd3) or cubic feet (ft3) for smaller amounts.
- (+W) Net Weight added to slab by rebar in pounds (lbs). This accounts for displaced concrete by volume.
- (RW) Gross Weight of Rebar in pounds (lbs)
- (CD) Gross Weight of Concrete Displaced in (lbs)
The Math / Science
Rebar weighs more than concrete and it takes up space in a concrete slab. When you add rebar to a slab or other concrete form (e.g. wall), you add weight and reduce the amount of concrete to fill the form. This calculator:
- Computes the weight and volume of rebar. The volume can be reduced from the volume of concrete in the slab.
- Computes the weight of the concrete equal to the volume of the rebar.
- Computes the difference between the weight of the rebar and the displaced concrete to provide the weight added by adding rebar. This can be added to the weight of the slab.
Density of Rebar vs Concrete:
- Density of Rebar: 7841.6 kg/m³
- Density of Concrete: 2400.0 kg/m³
General Rebar Information
Rebar is short for reinforcing bar. Rebar is a roughly circular steel bar with ribs used to provide added tensile strength to concrete structures. Rebar is put in place before concrete is poured. When the concrete has hardened, the concrete around the rebar ribs keep the rebar in place. Rebar and concrete expand similarly with temperature variations. This all has the net result of substantially added tensile strength when rebar is part of the concrete form. Carbon steel is the most commonly used material for rebar, which may also be coated with zinc or epoxy resin.
Rebar is laid out in grids, crisscrossed patterns of rebar, tied at the intersections where runs of rebar touch. The grids have spacing between the rebar rows, and they are placed within the concrete form by a specified inset from the edge of the concrete. Multiple parallel grids, at uniform space intervals, are referred to as rebar mats.
Rebar Terms
- Rebar - reinforcing steel bar.
- Stick - one length of rebar. In the U.S., the most common lengths of rebar sticks are 20', 40' and 60'.
- Lapping - when two sticks of rebar are overlapped and bound together.
- Lapping Factor - the multiple of a rebar diameter used to specify appropriate rebar lapping length.
- Mat - a crisscross grid of rebar sticks. There may be more than one mat with space in between mats.
- Size - the indicator of the diameter of rebar sticks. Note: guage is not a correct term for rebar.
Rebar Size
In the United States, rebar sizes are in increments of 1/8th inches in diameter. Therefore, size 4 is 4/8th of an inch, which is 1/2", and size 8 is a full inch in diameter. Based on this and the density of steel used in rebar, the Rebar Size Table contains reasonably accurate specifications of rebar linear weight and lateral (face) area based on rebar size.
Rebar Lapping
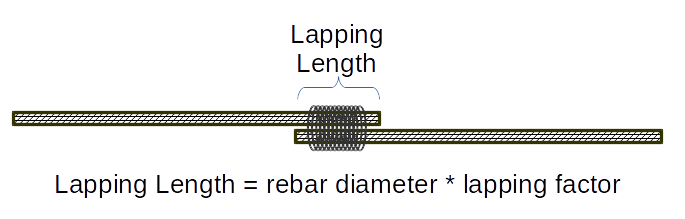
The most common lengths of pre-cut rebar in the United States are 20`, 40' and 60'. These are known as rebar sticks. When the dimensions of a slab, wall or other form exceed the length of a single stick of rebar, it is required to overlap and tie rebar pieces to create the added length. This process is called lapping, and the length of the overlapping rebar is the rebar lapping length. The length of the lap is specified by a "Lapping Factor (LF)" which is often 40 or 60 times the diameter of the rebar. Engineering specifications of a lapping factor should always be applied.
Rebar Tools
A class of rebar tools, both powered and manual, have been developed to aid construction workers in working with rebar. These include the following:
- Rebar Cutters are used to cleanly and safely cut sections of rebar.
- Rebar Benders are used to bend rebar sticks precisely to fit into concrete forms.
- Rebar Tiers are used to tie rebar grid intersections and for rebar lapping.
Equations and Data Items
Calculators
Collections
- Comments
- Attachments
- Stats
No comments |

